Carbon quantum dots: Synthesis and correlation of luminescence behavior with microstructure
-
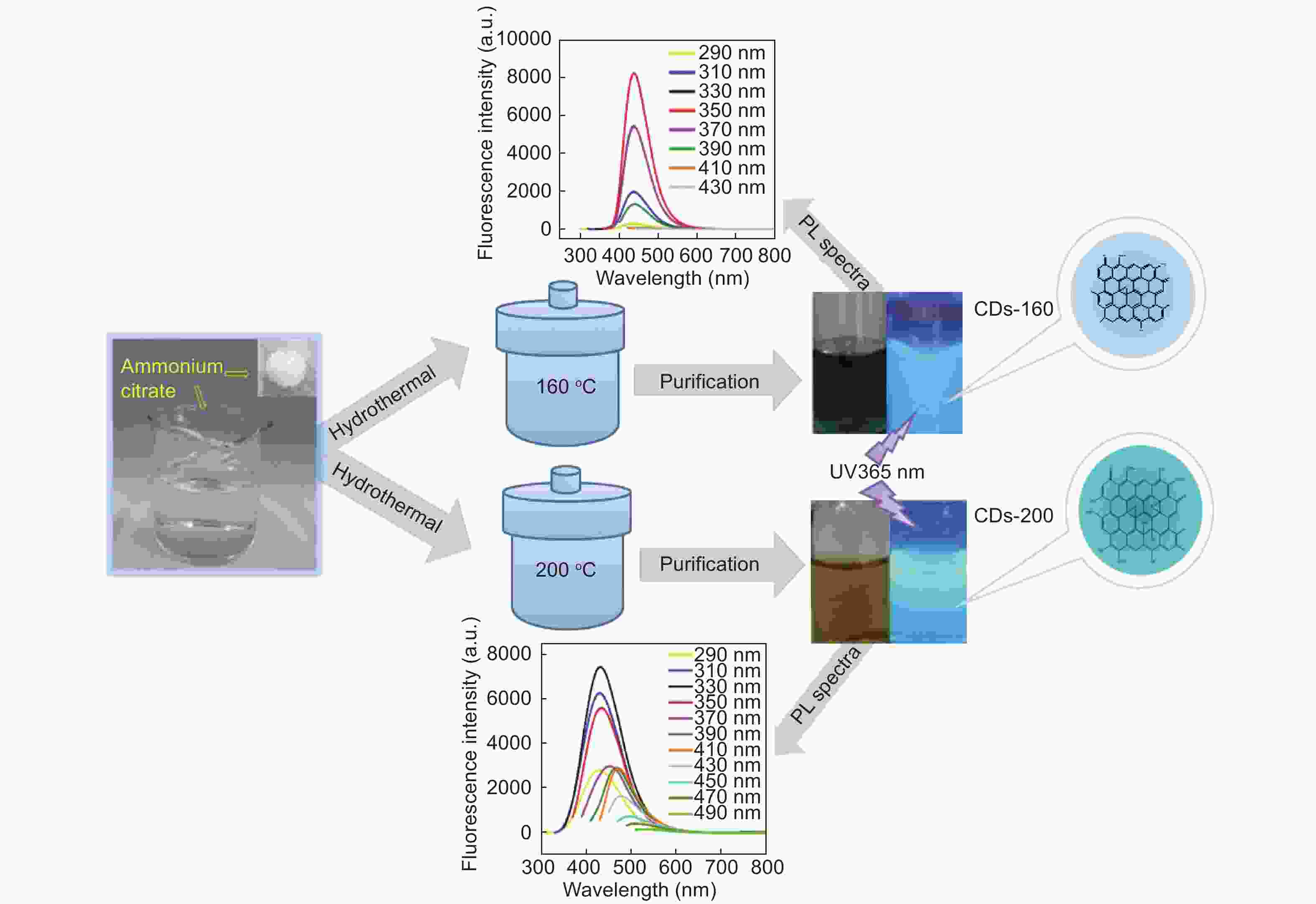
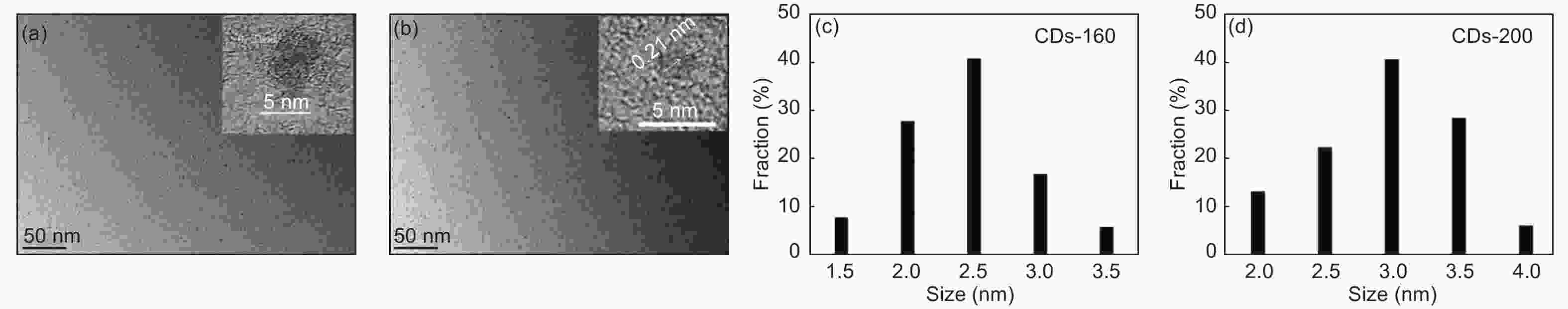
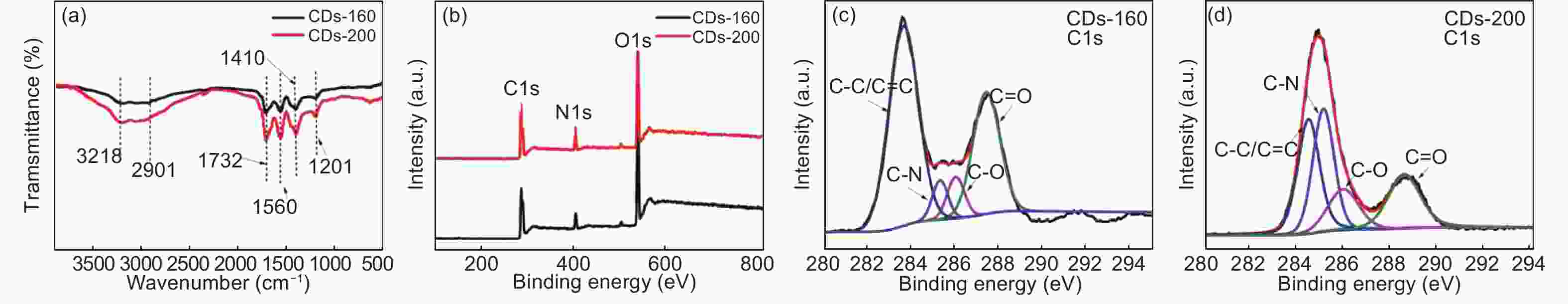
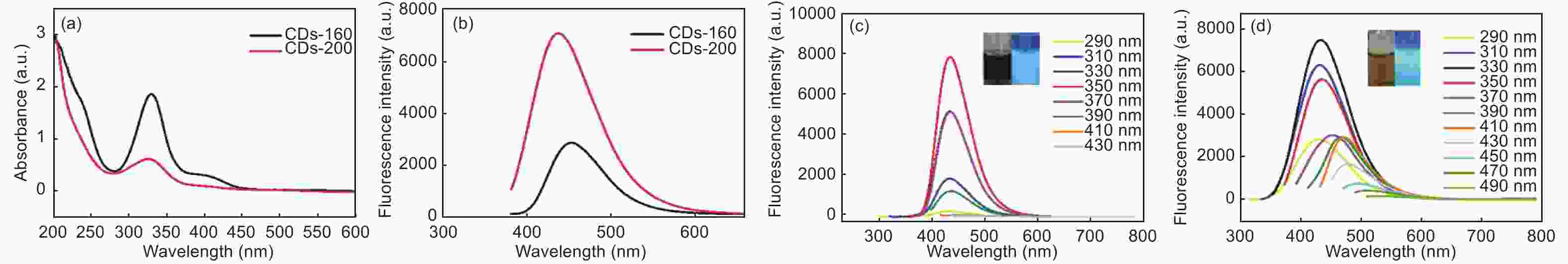
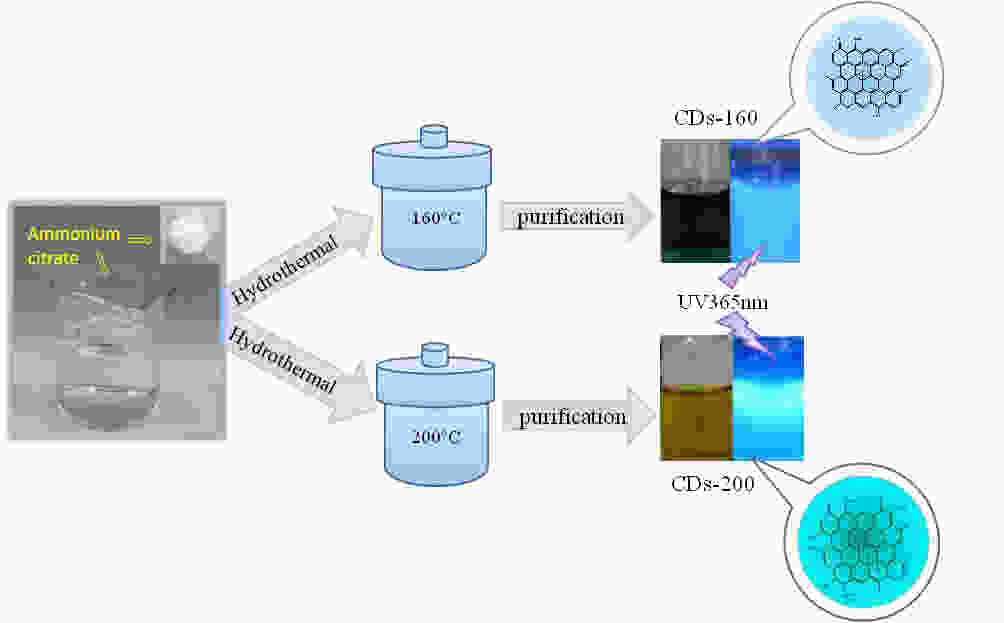
摘要: 以柠檬酸铵为原料采用一步水热法,通过改变反应温度合成出了两种分别具有激发波长独立和激发波长依赖荧光的碳量子点。通过考察两类碳量子点的物理、化学性质以及光学性能,可以推断碳点的结构与荧光发射之间的关系,最终研究碳量子点产生不同发光行为的原因。结果发现升高合成温度可以在碳量子点中引入更多的氧、氮杂原子,增加了结构缺陷(杂原子的化学态)的总量,并调变了各类化学态含量比。正是由于两种碳量子点的结构缺陷含量比例的不同,导致了碳量子点发光行为不同。合成温度高的碳量子点所含的各类结构缺陷含量比例较为均衡使得其呈现激发波长依赖性荧光;合成温度低的碳量子所含结构缺陷总量不高且主要以某种形式(如C=O)存在,是其拥有激发独立发光行为的主要原因。同时由于合成温度高的碳量子点所含的含氮基团的增加,使得碳量子点拥有更强的荧光发射。进一步考察还发现其具有非常优良的稳定性,因此可以预期有很好的应用前景。Abstract: Two kinds of carbon quantum dots, C-dots-160 and C-dots-200 with different fluorescence luminescence behaviors were synthesized by a one-step hydrothermal method at 160 and 200 °C, respectively, using ammonium citrate as the raw material. The relationship between the microstructure of the C-dots and the fluorescence emission behavior was investigated. Results indicate that an increase of synthesis temperature introduces more oxygen and nitrogen atoms into the C-dots, increasing the total number of structural defects and altering their concentation ratio . It is this ratio difference in the two C-dots that causes their different luminescence behaviors. The proportion of several types of defects in the C-dots-200 are relatively balanced, leading to excitation wavelength-dependent fluorescence while the most abundant defects in C-dots-160 are in the form of C=O, which is the main reason for its excitation independent luminescence behavior. The number of structural defects in C-dots-160 is less than in C-dots-200 and the latter has the stronger fluorescence emission.
-
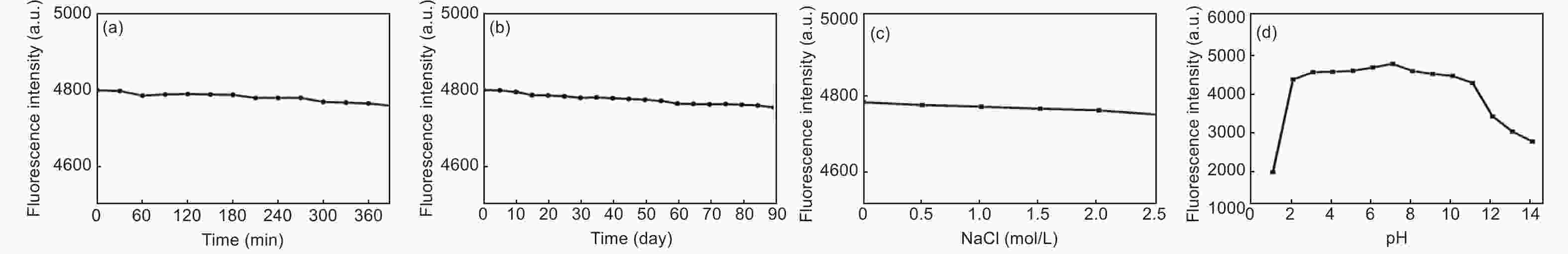
Figure 5. (a) Effect of time under UV irradiation of 365 nm, (b) effect of time at room temperature, (c) effect of ionic strength (ionic strength were controlled by various concentrations of NaCl aqueous solution) and (d) effect of pH (the pH was adjusted with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide) on fluorescence intensity of CDs-200.
-
[1] Sun Y P, Zhou B, Lin Y, et al. Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2006,128(24):7756-7757. doi: 10.1021/ja062677d [2] Molaei M J. Carbon quantum dots and their biomedical and therapeutic applications: a review[J]. RSC Advances,2019,9(12):6460-6481. doi: 10.1039/C8RA08088G [3] Li H T, He X D, Kang Z H, et al. Water-soluble fluorescent carbon quantum dots and photocatalyst design[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2010,49(26):4430-4434. doi: 10.1002/anie.200906154 [4] Wang H, Sun P F, Cong S, et al. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots for “green” quantum dot solar cells[J]. Nanoscale Research Letters,2016,11(1):27-33. doi: 10.1186/s11671-016-1231-1 [5] Fang L Y, Zhang L, Chen Z Z, et al. Ammonium citrate derived carbon quantum dot as onoff-on fluorescent sensor for detection of chromium(VI) and sulfites[J]. Materials Letters,2017,191(15):1-4. [6] Han G M, Zhao J, Zhang R L, et al. Membrane penetrating carbon quantum dots for imaging nucleic acid structures in live organisms[J]. Angew Chenu Int Ed,2019,58(21):7087-7091. doi: 10.1002/anie.201903005 [7] Athika M, Prasath A, Duraisamy E, et al. Carbon quantum dots derived from denatured milk for efficient chromium-ion sensing and supercapacit or applications[J]. Materials Letters,2019,241(1):156-159. [8] Bourlinos A B, Stassinopoulos A, Anglos D, et al. Surface functionalized carbogenic quantum dots[J]. Small,2008,4(4):455-458. doi: 10.1002/smll.200700578 [9] Li X M, Zhang S L, Kulinich S A, et al. Engineering surface states of carbon dots to achieve controllable luminescence for solid-luminescent composites and sensitive Be2+ detection[J]. Scientific Reports,2014,4(5):1-8. [10] Ding H, Yu S B, Wei J S, et al. Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism[J]. ACS nano,2016,10(1):484-491. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b05406 [11] Zhao Q L, Zhang Z L, Huang B H, et al. Facile preparation of low cytotoxicity fluorescent carbon nanocrystals by electrooxidation of graphite[J]. Chemical Communications,2008,7(41):5116-5118. [12] Baker S N, Baker G A. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2010,49(38):6726-6744. doi: 10.1002/anie.200906623 [13] Krysmann M J, Kelarakis A, Dallas P, et al. Formation mechanism of carbogenic nanoparticles with dual photoluminescence emission[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2012,134(2):747-750. doi: 10.1021/ja204661r [14] Nie H, Li M J, Li Q S, et al. Carbon dots with continuously tunable full-color emission and their application in ratiometric pH sensing[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2014,26(10):3104-3112. doi: 10.1021/cm5003669 [15] Fang L Y, Xu Q, Zheng X, et al. Soy flour-derived carbon dots: facile preparation, fluorescence enhancement, and sensitive Fe3+ detection[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research,2016,18(8):1-13. -





 下载:
下载: