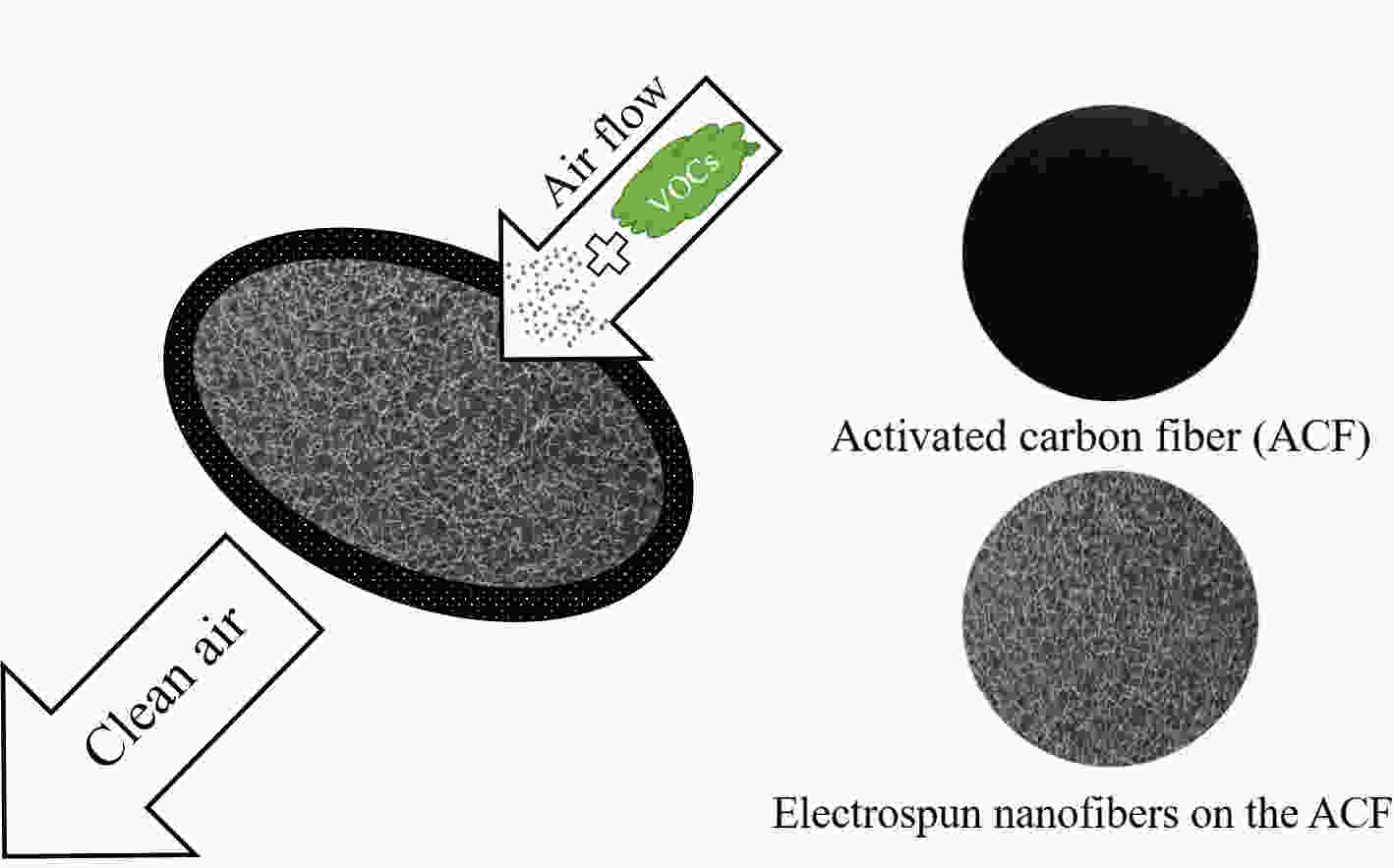
Hybridization of activated carbon fiber cloth with electrospun nanofibers for particle filtration
-
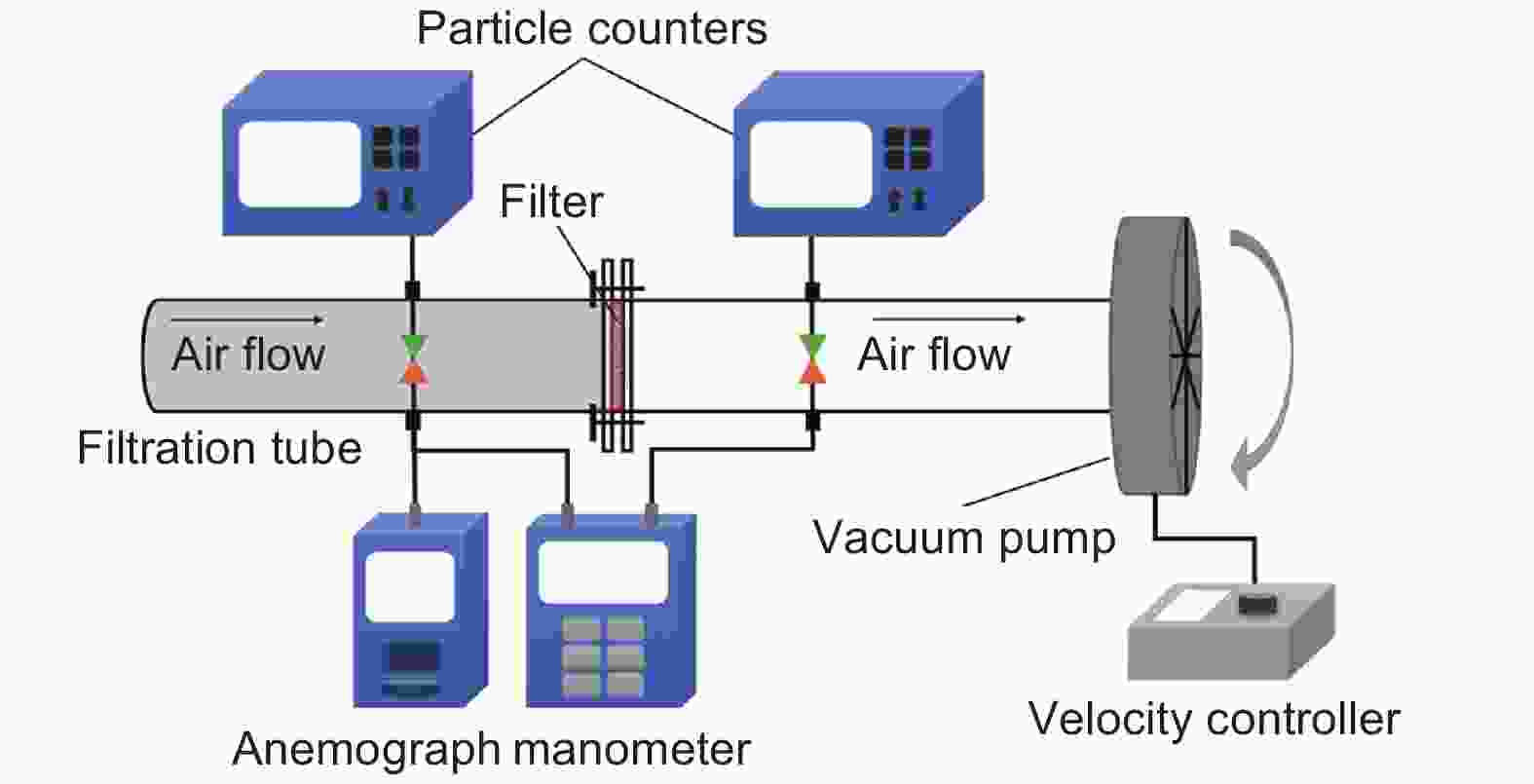
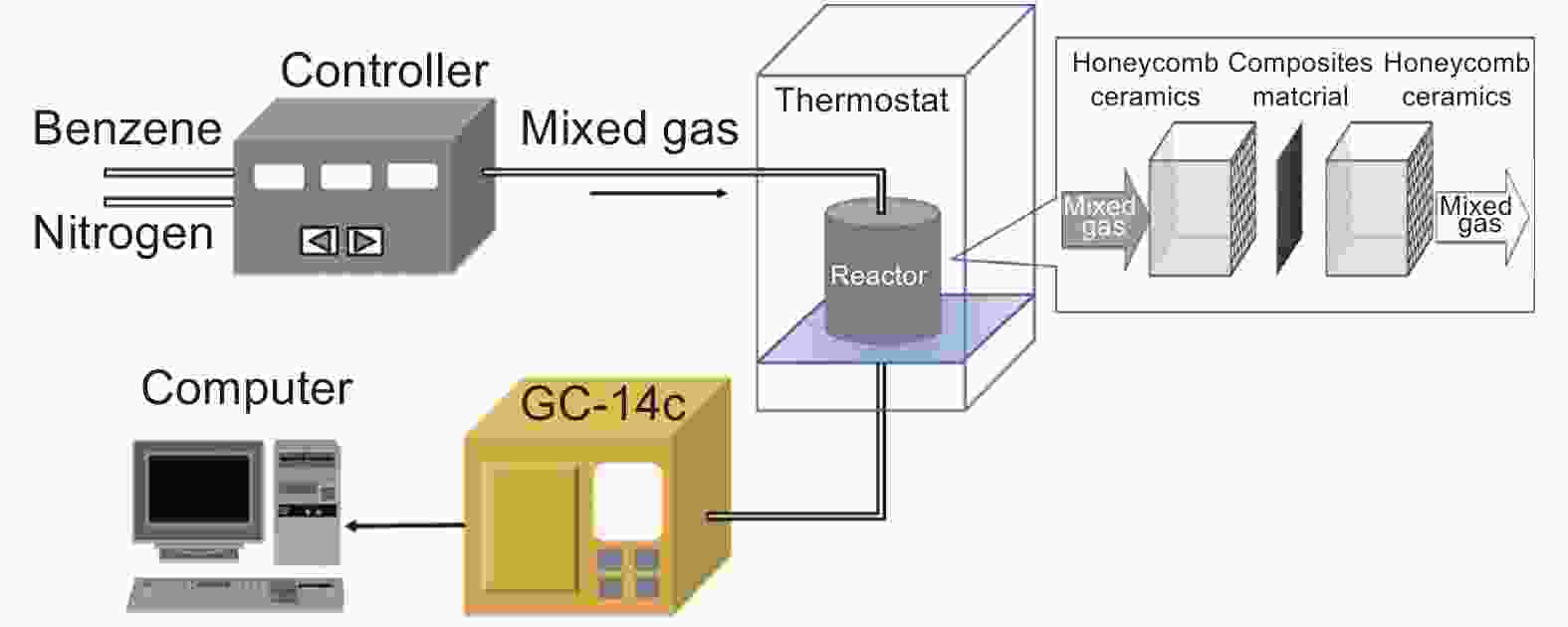
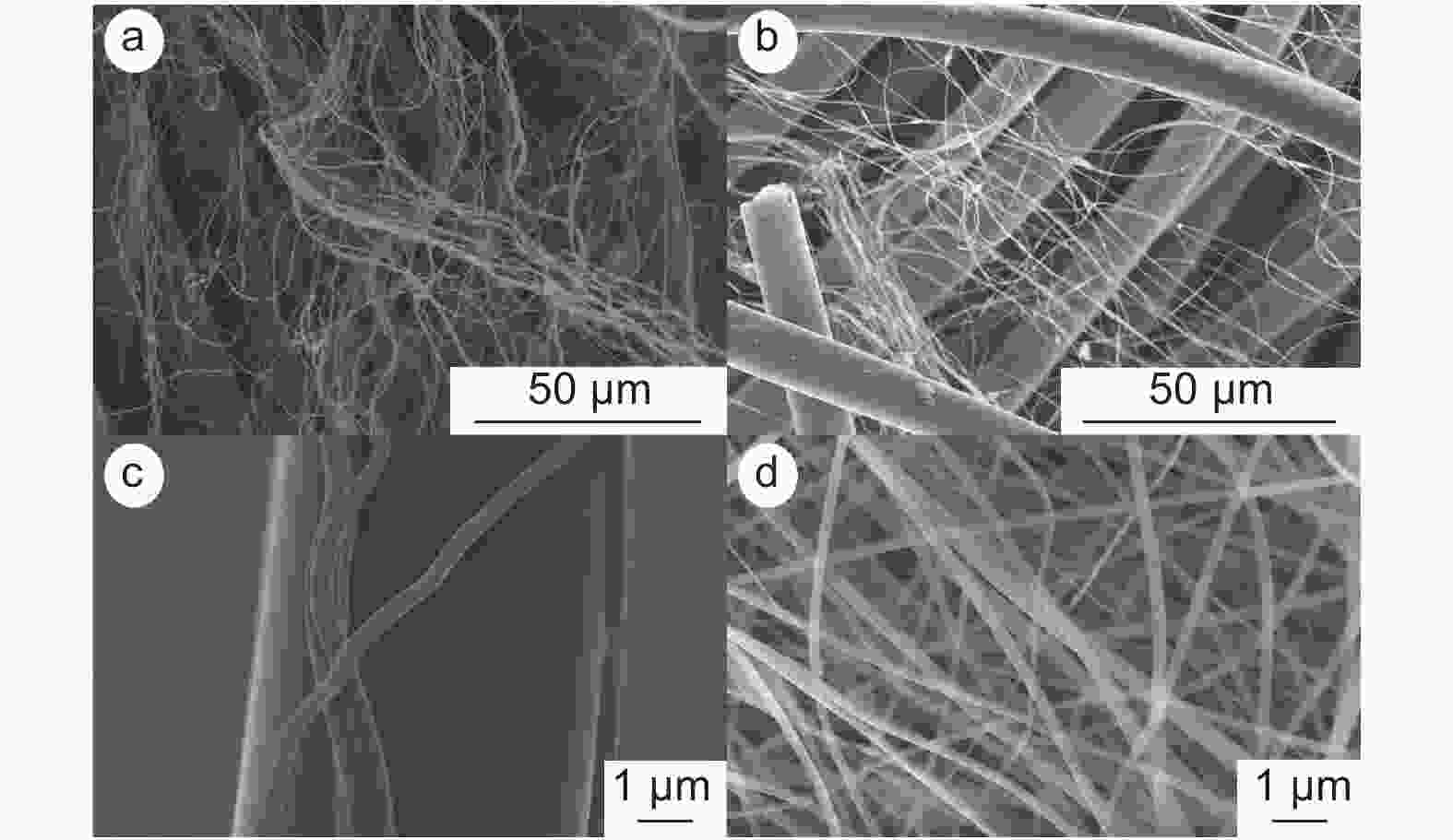
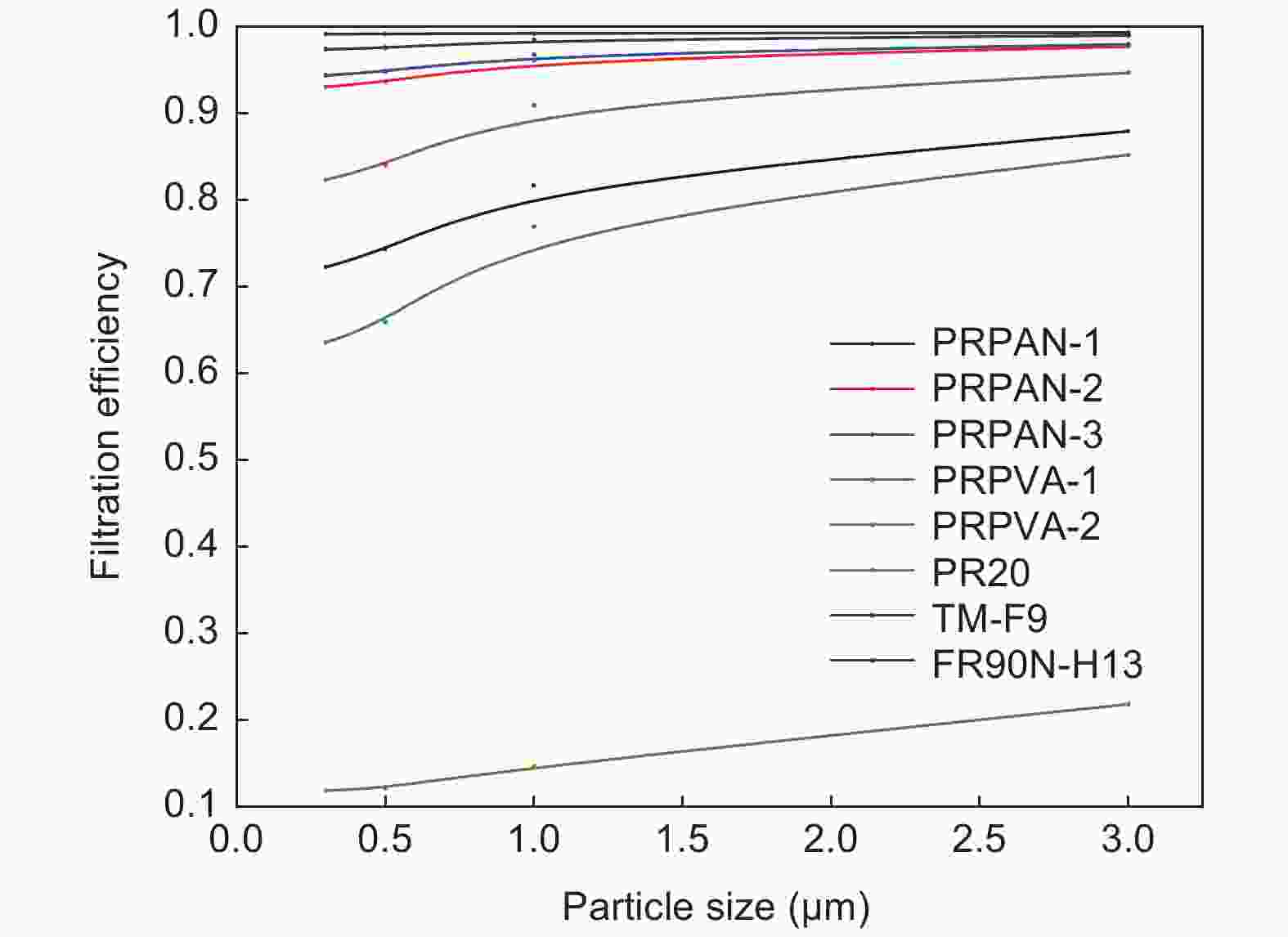
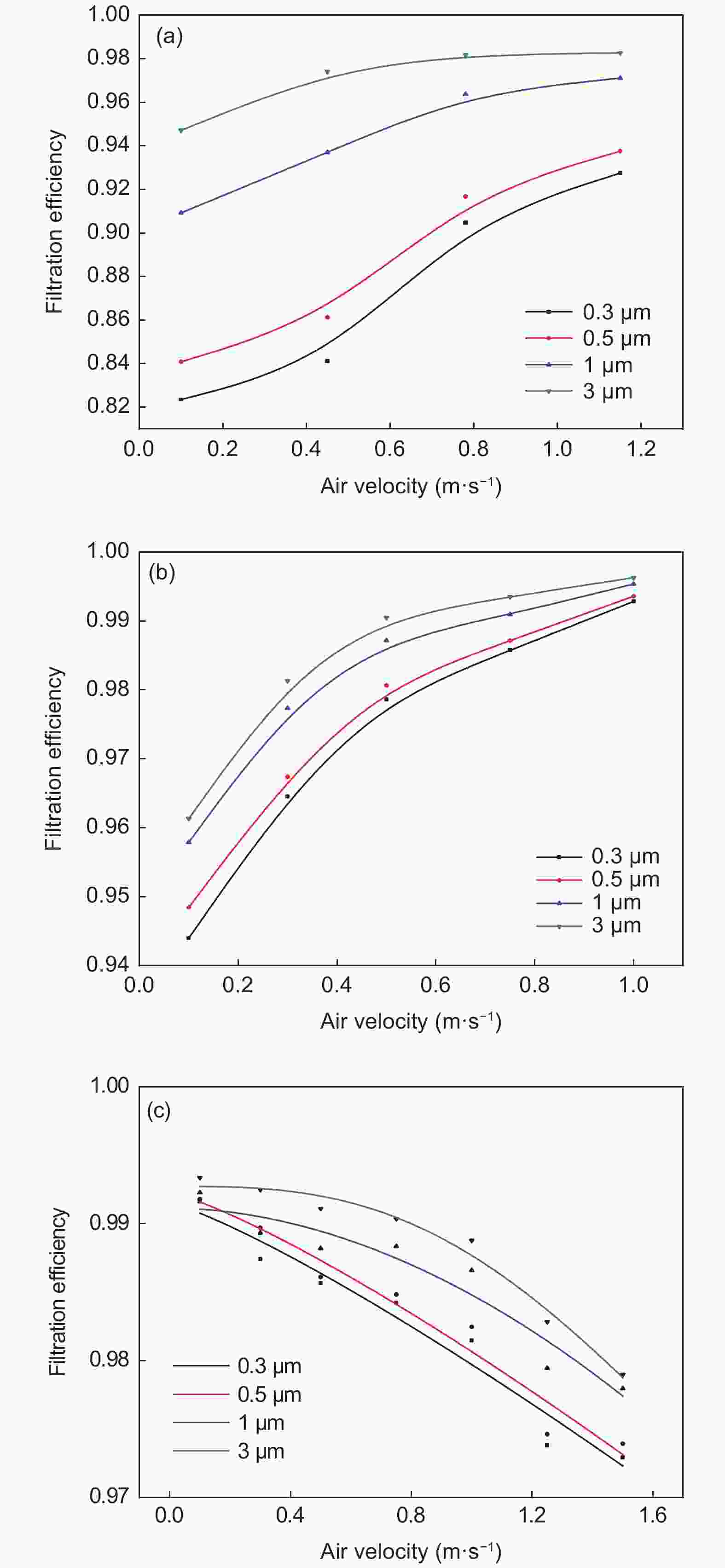
摘要: 活性炭纤维具有较高的吸附容量而被用于挥发性有机物的治理,而静电纺丝纤维对颗粒物具有较好的拦截能力可望用于过滤材料。本文采用高压静电纺丝的方法,将聚乙烯醇和聚丙烯腈纳米纤维纺丝至酚醛树脂基活性炭纤维布上获得了2种杂化纤维材料。通过颗粒物过滤测试系统评价了杂化纤维材料的过滤性能,结果表明样品的过滤效率与电纺丝纤维量呈正相关。由于电纺丝纤维引入的压电效应,使得样品的过滤效率随着气流流速的增加而提高。杂化纤维材料还具有较好的挥发性有机物吸附性能。这表明活性炭纤维布与电纺纤维的杂化材料在空气污染治理方面将具有较好的应用前景。Abstract: Activated carbon fibers (ACFs) have high adsorption capacities and can be used in the treatment of benzene, while electrospun nanofibers are expected to be used as a filtration material. In this work, two hybrids of electrospun nanofibers and ACF cloth were prepared by electrospinning polyvinyl alcohol and polyacrylonitrile nanofibers into a phenolic resin-based ACF cloth. The filtration performance of the two hybrids was evaluated. Results indicate that there is a positive correlation between the filtration efficiency and the amount of electrospun nanofibers in the hybrid. The filtration efficiency increases with increasing air velocity, which is attributed to a piezoelectric effect introduced by the electrospun nanofibers. The hybrids have a good adsorption capacity for benzene, which suggests that the materials are promising for treating air pollution.
-
Key words:
- Electrospun nanofibers /
- Activated carbon cloths /
- Air particles filtration /
- Benzene /
- Adsorption
-
Table 1. Features of electrospun nanofibers/phenolic resin based carbon fibers hybrid cloths
samples Time of electrospinning(min) Mass of ACFC(g) Mass of nanofibers(g) Areal density(mg·(cm2)−1) Mass ratio of nanofibers/hybrid cloths PRPVA-1 1.5 0.552 0.002 7.74 0.36% PRPVA-2 10 0.552 0.007 7.78 1.25% PRPAN-1 3.5 0.552 0.002 9.69 0.36% PRPAN-2 15 0.552 0.007 10.48 1.25% PRPAN-3 28 0.552 0.014 11.18 2.47% Table 2. Calculate adsorption capacity of samples
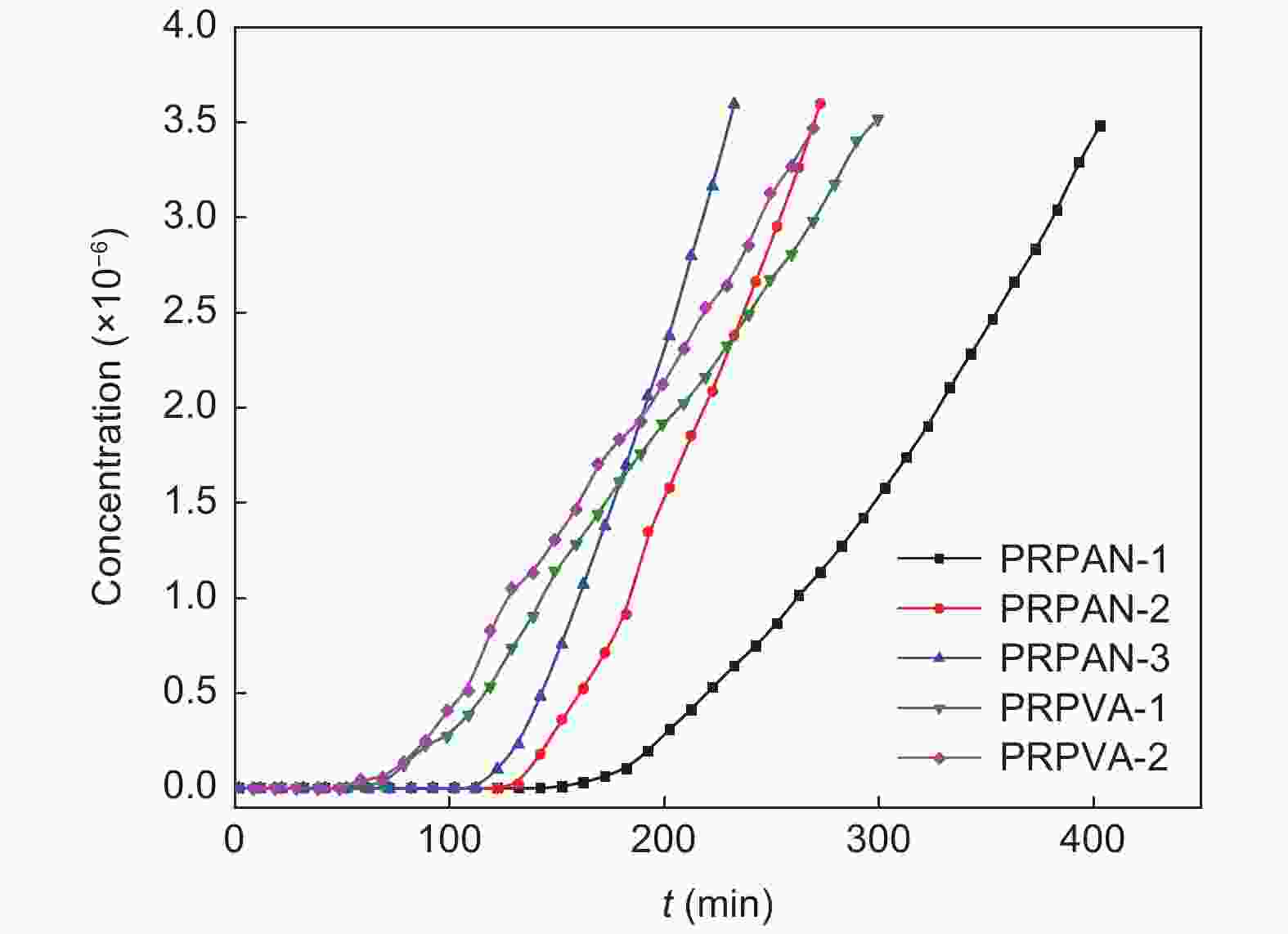
Sample Breakthrough time
(min)Adsorption capacity
(mg·g−1)PR20 370 202 PRPAN-1 383 201 PRPAN-2 272 131 PRPAN-3 232 101 PRPVA-1 299 188 PRPVA-2 269 142 -
[1] Pope C A, Burnett R T, Thun M J, et al. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution[J]. The Journal of the American Medical Association,2002,287(9):1132-1141. doi: 10.1001/jama.287.9.1132 [2] Seaton A, Macnee W, Donald son K, et al. Particulate air pollution and acute health effects[J]. Lancet,1995,345(8943):176-178. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(95)90173-6 [3] Brauner E V, Forchhammer L , Moller P, et al. Indoor particles affect vascular function in the aged filtration-based intervention study[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2008,177(4):419-425. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200704-632OC [4] Dwivedi P, Gaur V, Sharma A, et al. Comparative study of removal of volatile organic compounds by cryogenic condensation and adsorption by activated carbon fiber[J]. Separation & Purification Technology,2004,39(1-2):23-37. [5] Boskovic L, Agranovski I E. Removal of Fine Particles on Fibrous Filters [M]. Environanotechnology. 2010: 245-257. [6] Wang C S, Otani Y. Removal of nanoparticles from gas streams by fibrous filters: A review[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2012,52(1):5-17. [7] Wang C S. Electrostatic forces in fibrous filters—a review[J]. Powder Technology,2001,118(1-2):166-170. doi: 10.1016/S0032-5910(01)00307-2 [8] Pan Z, Liang Y, Tang M, et al. Simulation of performance of fibrous filter media composed of cellulose and synthetic fibers[J]. Cellulose,2019,26(12):7051-7065. doi: 10.1007/s10570-019-02605-8 [9] Barhate R, Ramakrishna S. Nanofibrous filtering media: Filtration problems and solutions from tiny materials[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2007,296(1-2):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2007.03.038 [10] Shin C, Chase G G, Reneker D H. Recycled expanded polystyrene nanofibers applied in filter media[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2005,262(1-3):211-215. [11] Hung C H, Leung W W F. Filtration of nano-aerosol using nanofiber filter under low peclet number and transitional flow regime[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2011,79(1):34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2011.03.008 [12] Sambaer W, Zatloukal M, Kimmer D. 3D modeling of filtration process via polyurethane nanofiber based nonwoven filters prepared by electrospinning process[J]. Chemical Engineering Science,2011,66(4):613-623. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2010.10.035 [13] Podgórski A, Ba Azy A, Gradoń L. Application of nanofibers to improve the filtration efficiency of the most penetrating aerosol particles in fibrous filters[J]. Chemical Engineering Ence,2006,61(20):6804-6815. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2006.07.022 [14] Lv D, Zhu M, Jiang Z, et al. Green electrospun nanofibers and their application in air filtration[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering,2018,303(12):336-354. [15] Guibo Y, Qing Z, Yahong Z, et al. The electrospun polyamide 6 nanofiber membranes used as high efficiency filter materials: Filtration potential, thermal treatment, and their continuous production[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2013,128(2):1061-1069. doi: 10.1002/app.38211 [16] Cao J, Cheng Z, Kang L, et al. Novel anti-fouling polyethersulfone/polyamide 66 membrane preparation for air filtration by electrospinning[J]. Materials Letters,2017,192(APR. 1):12-16. [17] Cai R R, Zhang L Z, Bao A B. Pm collection performance of electret filters electrospun with different dielectric materials-a numerical modeling and experimental study[J]. Building and Environment,2018,131:210-219. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2017.12.036 [18] Li Y, Yin X, Yu J, et al. Electrospun nanofibers for high-performance air filtration[J]. Composites Communications,2019,15:6-19. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2019.06.003 [19] Zhang Q, Liu F, Yang T Y, et al. Deciphering effects of surface charge on particle removal by TiO2 Polyacrylonitrile nanofibers[J]. Aerosol & Air Quality Research,2017,17(7):1909-1916. [20] Gorji M, Bagherzadeh R, Fashandi H. Electrospun Nanofibers in Protective Clothing [M]. Electrospun Nanofibers. 2017: 571-598. [21] Haider A, Haider S, Kang I K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry,2018,11(8):1165-1188. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.11.015 [22] Cheng Y, Wang C, Zhong J, et al. Electrospun polyetherimide electret nonwoven for bi-functional smart face mask[J]. Nano Energy,2017,34:562-569. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.03.011 [23] Bouchaala. Volatile organic compounds removal methods: A review[J]. American Journal of Biochemistry and Biotechnology,2012,8(4):220-229. doi: 10.3844/ajbbsp.2012.220.229 [24] Lillo-Ródenas M A, Cazorla-Amorós D, Linares-Solano A. Benzene and toluene adsorption at low concentration on activated carbon fibres[J]. Adsorption,2010,17(3):473-481. [25] Lillo-Ródenas M A, Cazorla-Amorós D, Linares-Solano A. Behaviour of activated carbons with different pore size distributions and surface oxygen groups for benzene and toluene adsorption at low concentrations[J]. Carbon,2005,43(8):1758-1767. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2005.02.023 [26] Chai X, Song X, He H, et al. Effects of adsorbate molecular space conformation on the adsorption capacity of porous carbon materials: A case study of propylene glycol methyl ether[J]. Sci Total Environ,2020,712(2019):135-495. [27] Li J, Lu R, Dou B, et al. Porous graphitized carbon for adsorptive removal of benzene and the electrothermal regeneration[J]. Environ Sci Technol,2012,46(22):12648-12654. doi: 10.1021/es303069j [28] Lu A H, Zheng J T. Study of microstructure of high-surface-area polyacrylonitrile activated carbon fibers[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci,2001,236(2):369-374. doi: 10.1006/jcis.2000.7425 [29] Yoon J S. Visualization of particle behavior within a porous medium: Mechanisms for particle filtration and retardation during downward transport[J]. Water Resources Research,2006,42(6):6417-6433. [30] Zhang J, Gong S, Wang C, et al. Biodegradable electrospun poly(Lactic Acid) nanofibers for effective Pm 2.5 removal[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering,2019,304(10):259-267. [31] Bae J, Baek I, Choi H. Efficacy of piezoelectric electrospun nanofiber membrane for water treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,307:670-678. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.125 [32] Zhang S, Rind N A, Tang N, et al. Electrospun Nanofibers for Air Filtration[M]. Electrospinning: Nanofabrication and Applications. 2019: 365-389. [33] Zhu M, Han J, Wang F, et al. Electrospun nanofibers membranes for effective air filtration[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering,2017,302(1):353-380. [34] Lillo-Ródenas M A, Fletcher A J, Thomas K M, et al. Competitive adsorption of a benzene–toluene mixture on activated carbon at low concentration[J]. Carbon,2006,44(8):1455-1463. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2005.12.001 [35] Baur G B, Yuranov I, Renken A, et al. Activated carbon fibers for efficient voc removal from diluted streams: The role of surface morphology[J]. Adsorption,2015,21(4):479-488. -





 下载:
下载: