The use of graphene and its composites to suppress the shuttle effect in lithium-sulfur batteries
-
摘要: 硫锂电池具有比能高达1675 mAh g−1、价格低廉、环保等优点,是一种具有良好应用前景的二次电池。但由于放电过程中多硫化物溶解产生的穿梭效应、硫的绝缘和硫电极的体积膨胀等原因导致锂硫电池的循环稳定性还不能满足工业化要求。石墨烯具有优异的导电性、超大的比表面积、良好的机械柔韧性和热化学稳定性,因此石墨烯及其衍生物成为全固态锂硫电池电极和改性隔膜的重要材料。本文综述了在全固态锂硫电池中,石墨烯的网络结构对电子转移非常有利,可以限制硫电极体积膨胀并促进离子迁移;同时作为改性隔膜的首选材料之一,石墨烯及其衍生物的六边形层状结构形成的锂离子输运通道能够捕获硫。总结了石墨烯及其衍生物抑制穿梭效应的机制,提出了石墨烯在锂硫电池中的发展策略和前景。Abstract: The lithium sulfur battery has a high theoretical capacity of 1675 mAh g-1, and is cheap and environmentally friendly, which make it a very promising secondary battery. However, its cycling stability cannot meet the requirements of industrialization due to the shuttle effect caused by the dissolution of polysulfides in the discharge process, the insulating nature of sulfur and the volume expansion of the sulfur cathode. Graphene has an excellent electrical conductivity, an extremely large specific surface area, good mechanical flexibility, and thermal and chemical stability, making it and its derivatives promising candidates to modify both the electrodes of an all-solid-state lithium-sulfur battery and the separator. The mechanisms, by which graphene and its derivatives inhibit the shuttle effect are summarized. The graphene network is very favorable for improving electron transfer rate, limiting volume expansion and facilitating lithium ion migration in the sulfur cathode of all-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries. As modifiers of the separator, the hexagonal layer structure of graphene and its derivatives forms channels for lithium-ion transport and sulfur capture. Development strategies for using graphene and its derivatives in lithium-sulfur batteries are proposed.
-
Key words:
- Graphene /
- Lithium-sulfur /
- Shuttle effect /
- All-solid-state /
- Modified layer
-
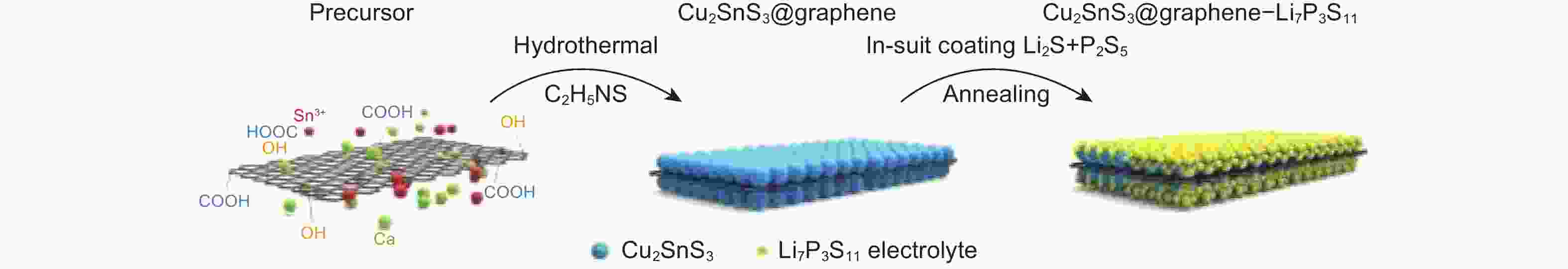
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the fabrication procedure of Cu2SnS3@graphene-Li7P3S11 nanocomposite, where the hydrothermal method was applied to synthesize Cu2SnS3@graphene composite and then Li7P3S11 electrolyte was coated on Cu2SnS3@graphene by an in-situ liquid-phase reaction, followed by an annealing treatment[47]. Copyright (2019) WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
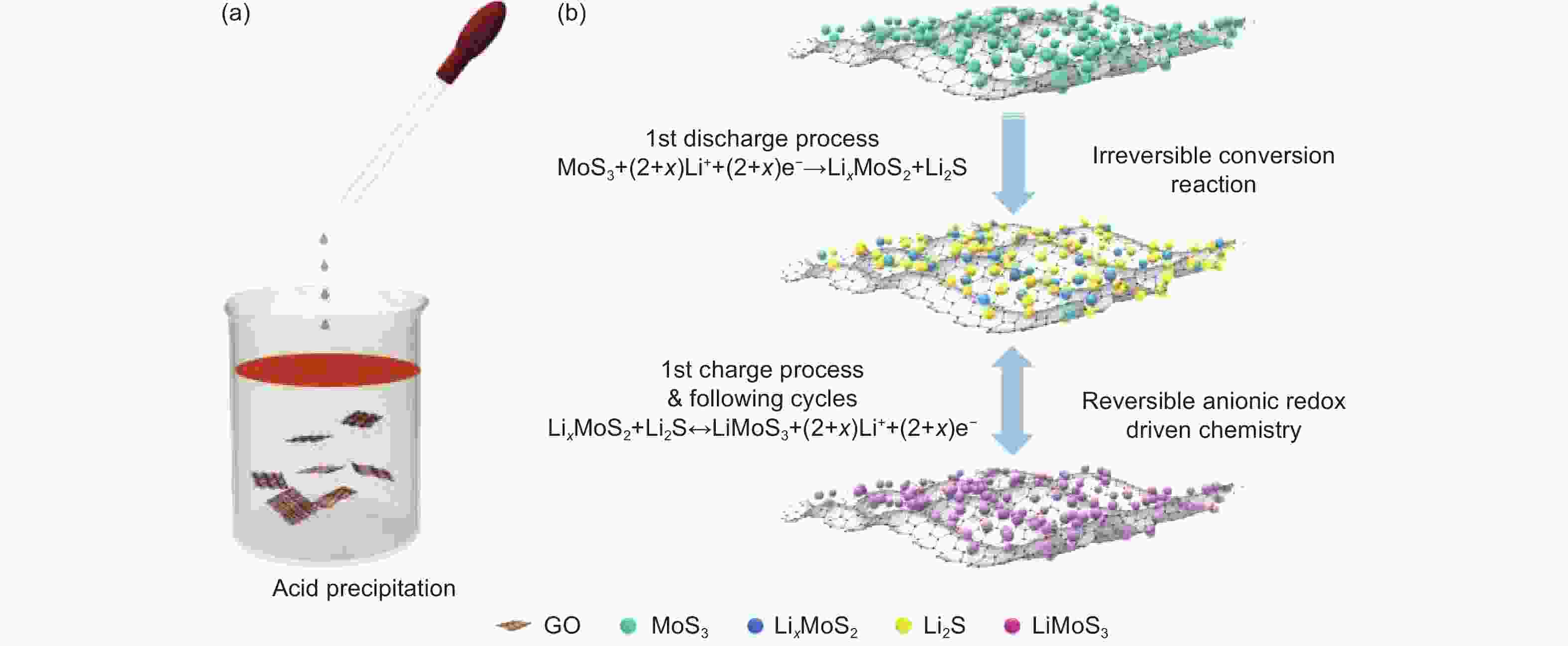
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of (a) synthesis process and (b) reaction mechanisms of rGO-MoS3 nanocomposites[42]. Copyright 2405-8297/© 2019 Elsevier B.V.
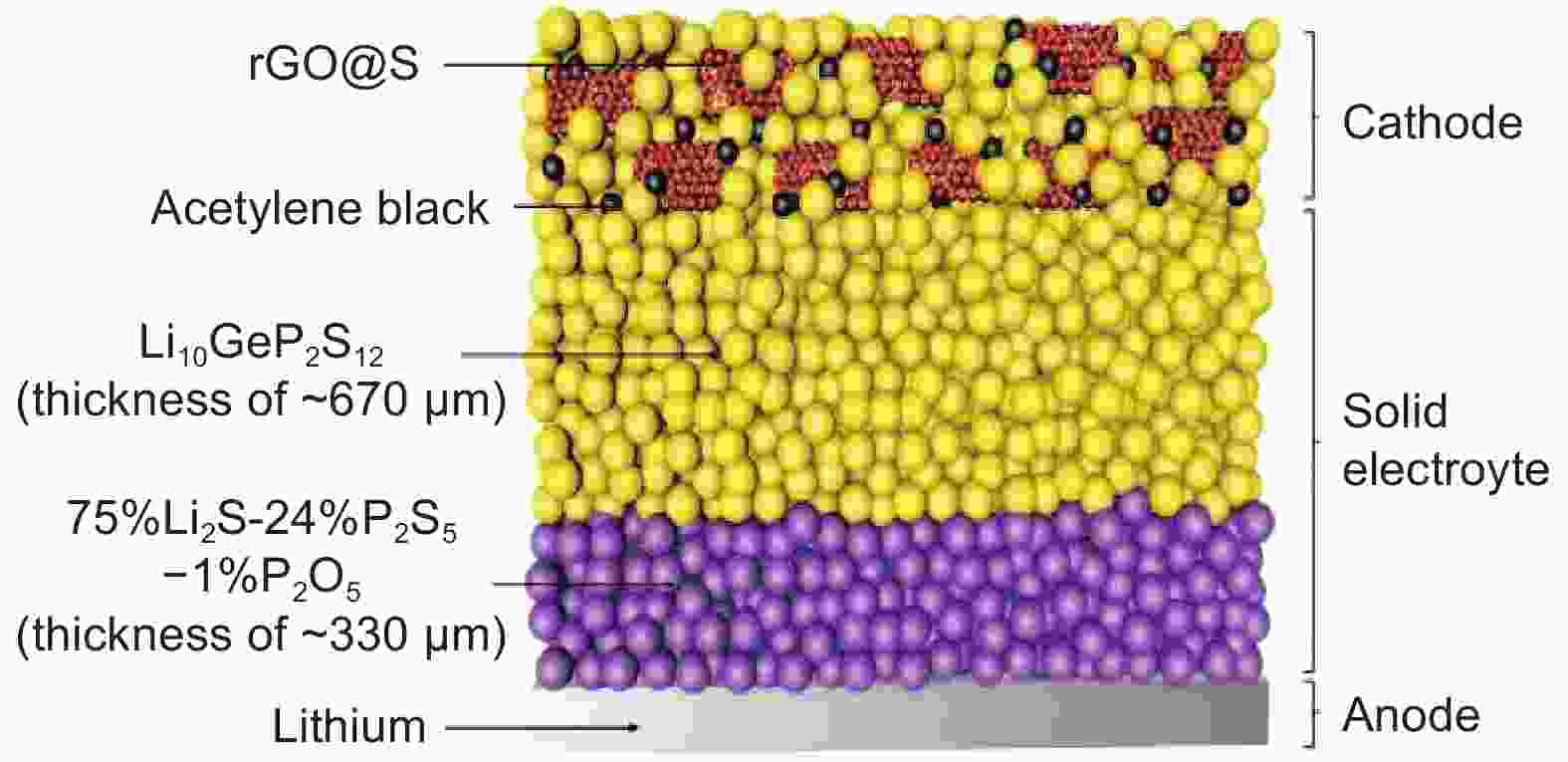
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of an all-solid-state LSB[52]. Copyrights 2017 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figure 4. TEM images of GO-PEG@C/S with a scale bar of (a) 100 nm and (b) 200 nm, (c) HAADF-STEM image of the yellow dotted area in (b), and the corresponding elemental mapping of (d) sulfur, (e) carbon and (f) oxygen[11]. Copyright © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017.
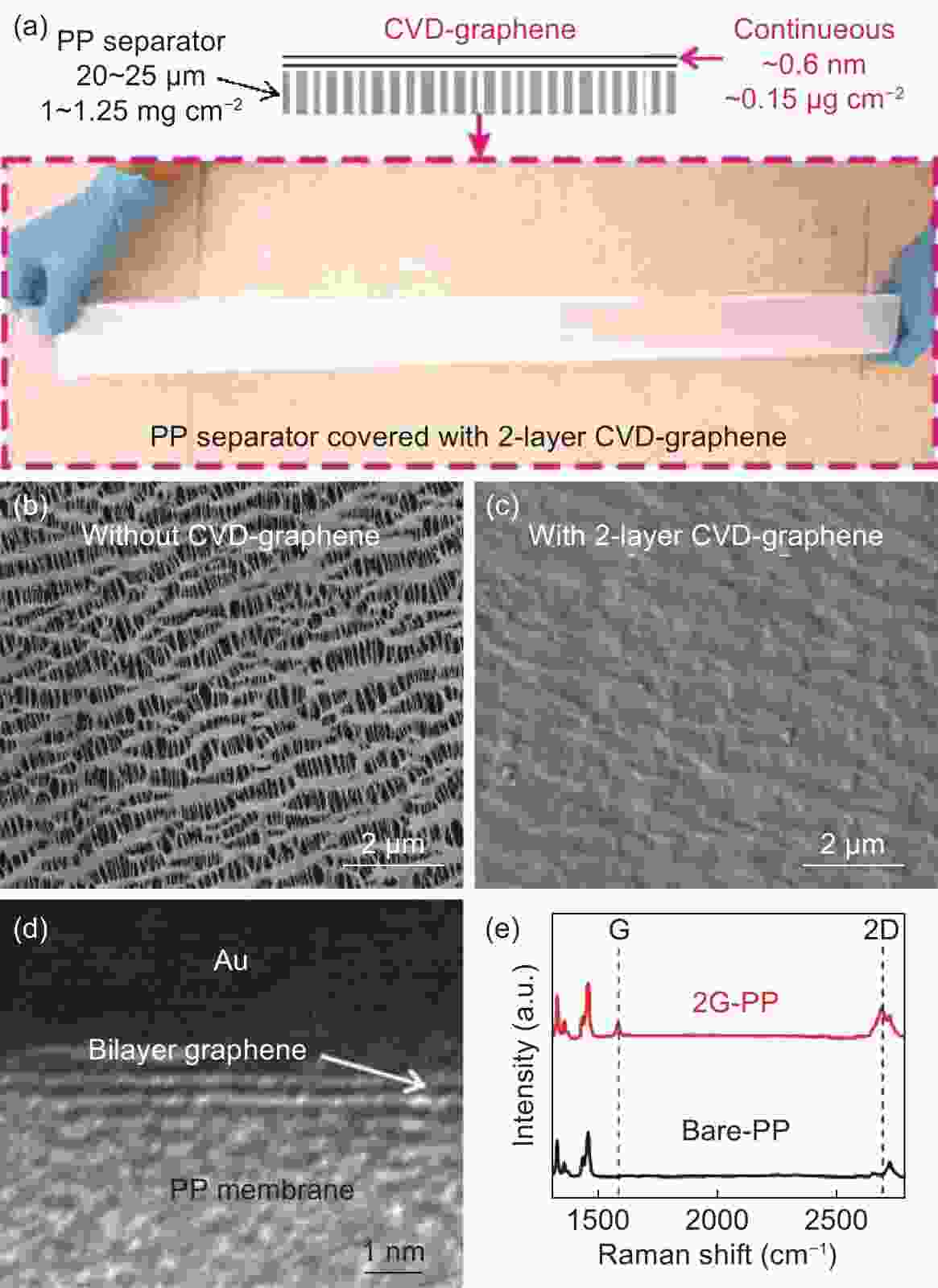
Figure 5. (a) Schematic of interlayers containing CVD-G film and photograph showing a PP separator covered with two layers of CVD-G with a total thickness of ~0.6 nm and area of 5 × 60 cm2, (b, c) SEM images of a bare-PP and 2G-PP separator, (d) TEM image showing a cross section of 2G-PP and (e) Raman spectra of bare-PP and 2G-PP[59]. The copyright © 2017 American Chemical Society.
Figure 6. (a) Schematic configuration of the synthesized GA–CNFs–Ni hybrids, schematic diagram of the LSBs with (b) pristine separator and (c) GA–CNFs–Ni coated separator[61]. The copyright© The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018.
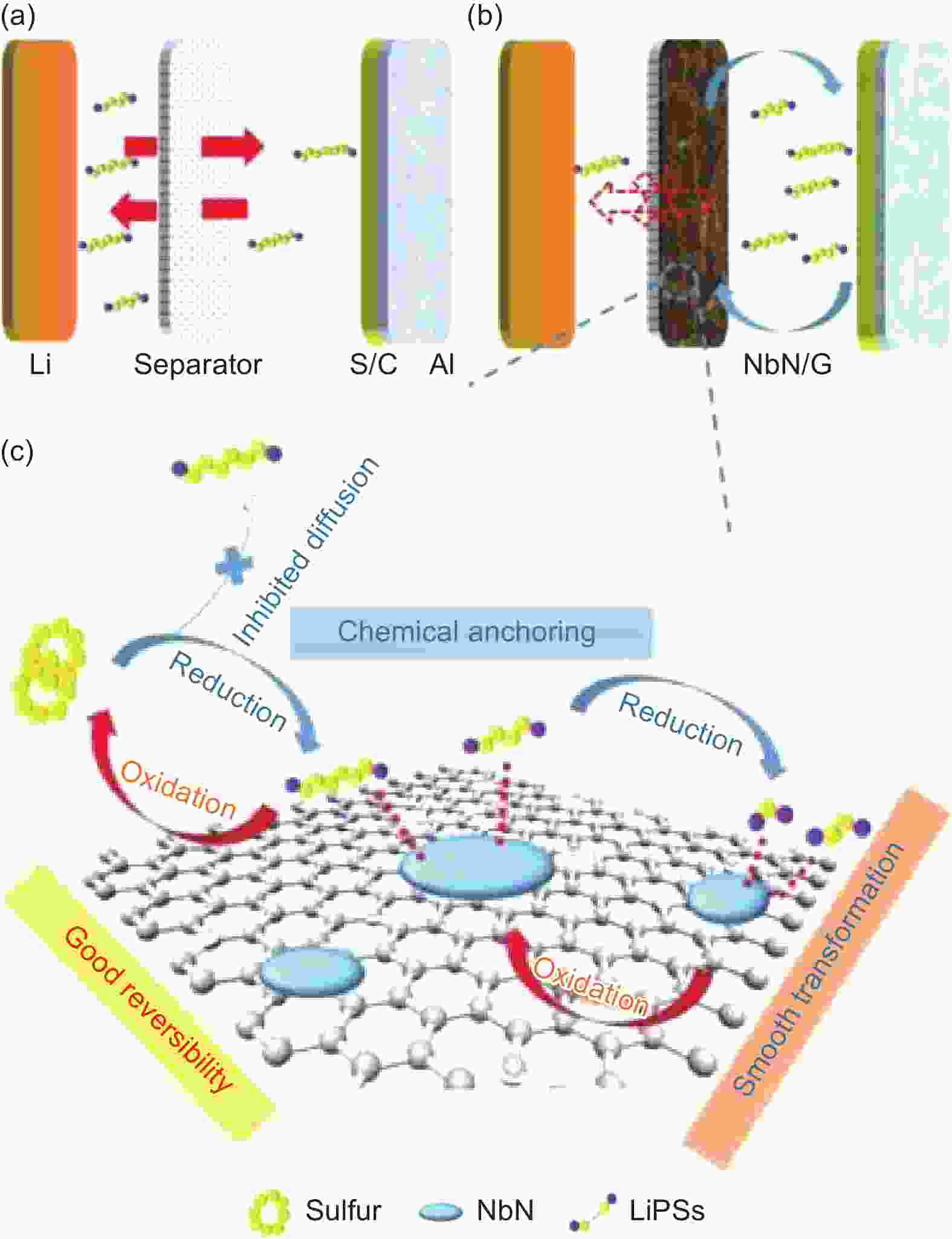
Figure 7. (a) Schematic of a conventional configuration for LSBs with a commercial PP separator, (b) an optimized configuration with a NbN/G interlayer between the separator and the sulfur cathode and (c) the key role of NbN nanoparticles on regulating the redox conversion process of LiPSs[75]. Copyright 2095-4956/© 2019 Science Press and Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Published by Elsevier B.V. and Science Press. All rights reserved.
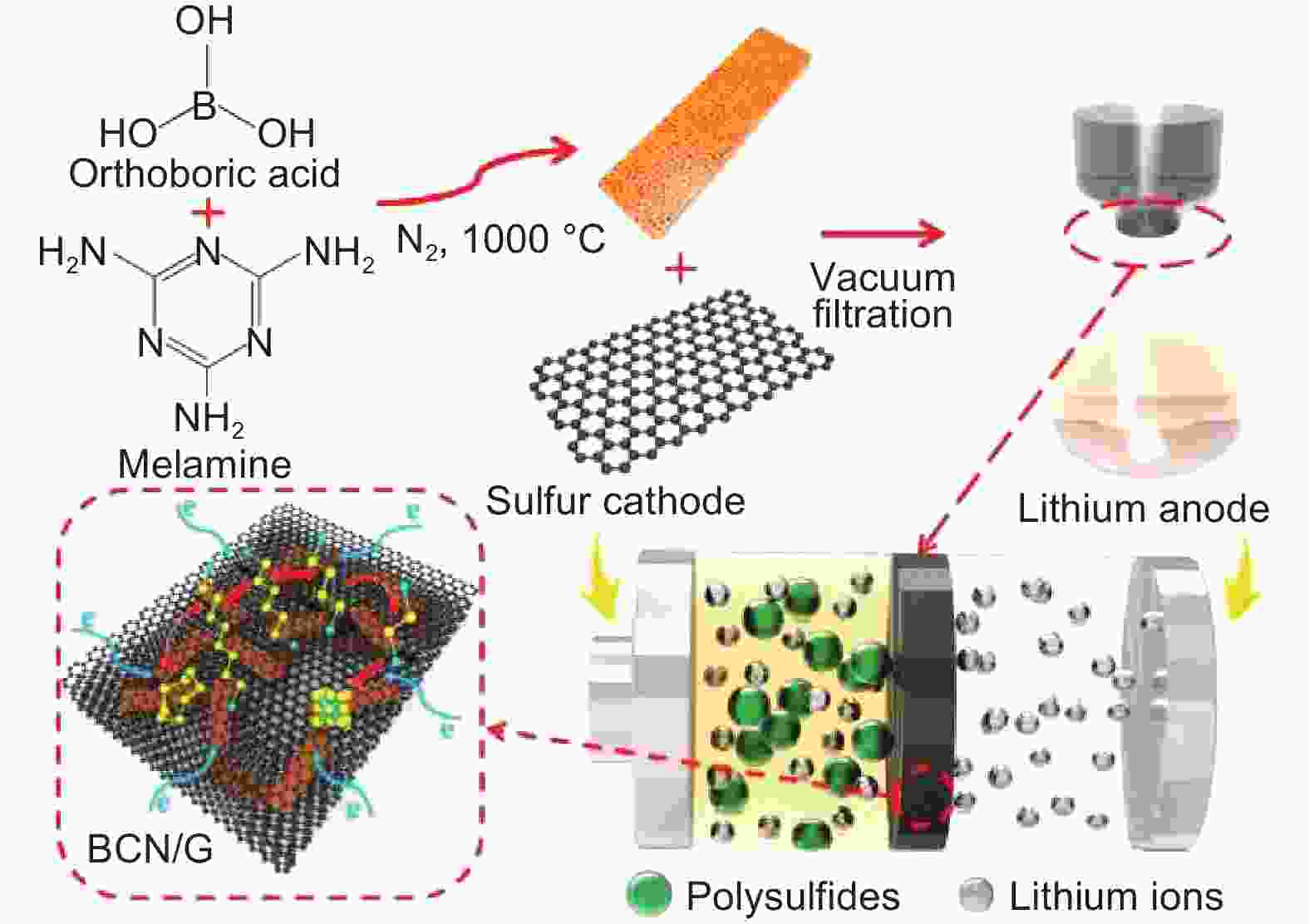
Figure 8. Schematic illustration of synthesizing the BCN/G modifier and electrode configuration of the LSBs with a BCN/G modified separator[77]. Copyright 1572-6657/ © 2019 Published by Elsevier B.V.
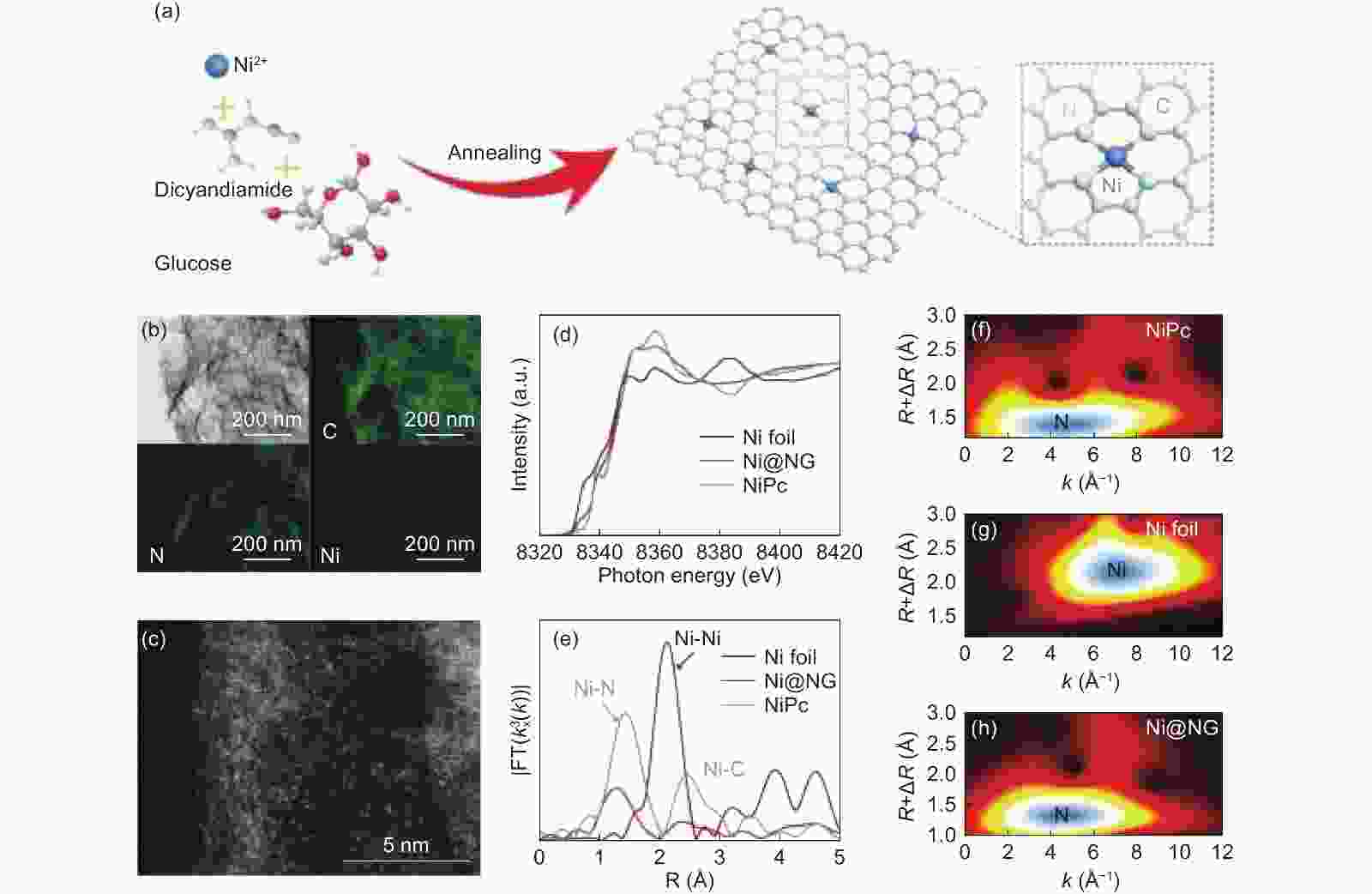
Figure 9. (a) Schematic illustration of the preparation of Ni@NG with the Ni-N4 sites, (b) TEM and the corresponding element mapping images of Ni@ NG (The grey, cyan, red, white, and blue balls represent C, N, O, H, and Ni atoms, respectively), (c) the sub-angstrom resolution HAADF-STEM image of Ni@NG, where the single Ni atoms present as bright dots, (d) XANES, (e) FT-EXAFS spectra, and (f–h) WT transform contour plots at Ni K edge of Ni@NG with respect to the reference samples[79]. Copyright. 2019 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
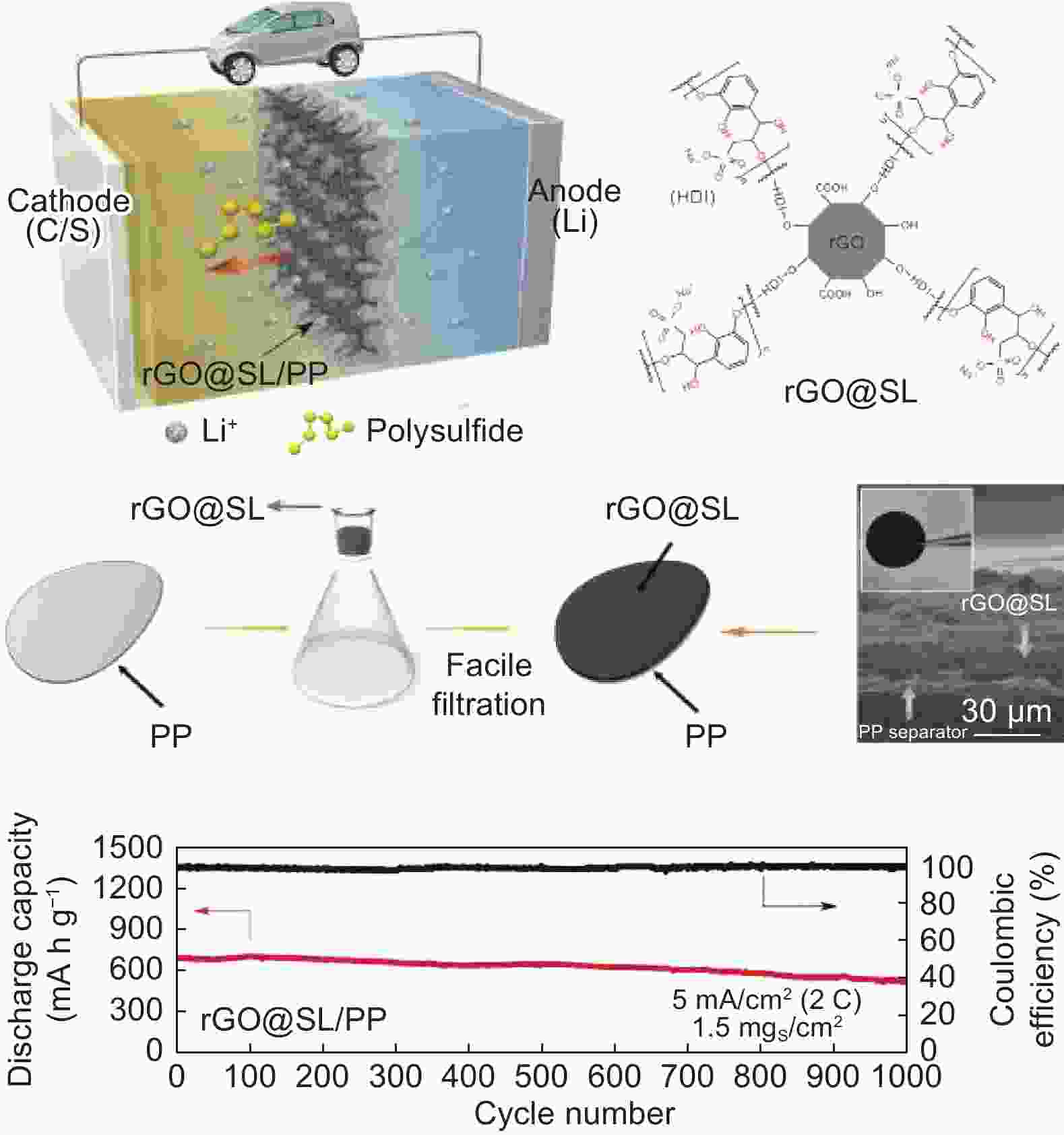
Figure 10. A graphene composite separator with abundant sulfonic groups was prepared by directly polymerizing hexamethylene diisocyanate with rGO and sodium lignosulfonates, followed by a simple filtration process. The rich negative charge in the composite separator effectively suppressed the translocation of the negatively charged polysulfide ions to enable highly robust LSBs[96]. The copyright @ 2018 Elsevier Inc.
Table 1. Mass loading or thickness of the coating layers of separators modified by graphene and its composites, and discharge and cycle performance of LSBs using them.
Coating layer Mass loading /mg cm−2 Initial specific capacity /mA h g−1 Cycle numbers Capacity decay rate /per cycle Current density Ref. GO/Nafion 0.053 1057 200 0.18% 0.1 C [4] GO/CNT 1.1 1370 300 0.17% 0.2 C [34] Graphene 1.3 933 500 0.064% 0.89 C [37] RGO/AC modified separator - 1078 100 0.39% 0.1 C [53] 2G 1.52×10-4 1035 1500 0.026% 0.5 C [59] Graphene@paper separator 0.008 817 200 0.225% 0.5 C [60] Sandwich-type nitrogen and sulfur codoped graphene-backboned porous carbon (NSGPC) 0.49 (21 μm) 890 500 0.074% 2 C [72] NbN/G 0.28 1079 300 0.096% 1 C [75] Oxygen doped carbon on the surface of reduced graphene oxide (ODC/rGO) 0.50 - 600 0.057% 1 C [78] Ni@NG 0.3 1059 500 0.044% 1 C [79] Fe-N-C/G 0.083 - 500 0.053% 0.5 C [83] GA-VOx/CB - 752 600 0.069% 1 C [85] ZnO/CNT/rGO 0.85 1061 150 0.18% 0.2 C [86] ZnO/ NDG 1 942 200 0.0499% 0.1 C [88] PG-Fe3O4 0.478 696 497 0.0376% 0.1 C [89] ReS2@NG 0.08−0.09 854 800 0.064% 2 C [91] rGO@CoSe2 0.49 1065 500 0.0856% 0.5 C [92] G@POF-Fe 35 μm 1120 250 0.0788% 0.2 C [93] Si3N4/rGO 23 μm 897 1000 0.054% 1 C [94] rGO@SL 0.2 707 1000 0.026% 2 C [95] Graphene/ Li-stuffed garnet solid-state electrolyte (SSE) 11 μm 1165 200 0.095% 0.5 C [96] Li4Ti5O12 (LTO)/graphene 0.346 - 500 0.0286% 1 C [99] Polypropylene/graphene oxide/Nafion 0.0532 1057 200 0.18% 0.1 C [100] Ti3C2Tx/GO - 904.5 300 0.103% 1 C [101] Graphene oxide 0.12 920 100 0.23% 0.1 C [102] MOF/GO 0.3 1126 500 0.058% 0.5 C [103] TiO2/graphene 0.097 1100 300 0.045% 0.5 C [104] -
[1] Tan S Y, Wu Y F, Kan S T, et al. A combination of MnO2-decorated graphene aerogel modified separator and I/N codoped graphene aerogel sulfur host to synergistically promote Li-S battery performance[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2020,348:136173. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136173 [2] Wutthiprom J, Phattharasupakun N, Sawangphruk M. Designing an interlayer of reduced graphene oxide aerogel and nitrogen-rich graphitic carbon nitride by a layer-by-layer coating for high-performance lithium sulfur batteries[J]. Carbon,2018,139:945-953. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.08.008 [3] Kong W B, Yan L J, Luo Y F, et al. Ultrathin MnO2/graphene oxide/carbon nanotube interlayer as efficient polysulfide-trapping shield for high-performance Li-S batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2017,27:1606663. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201606663 [4] Huang J Q, Zhang Q, Wei F. Multi-functional separator/interlayer system for high-stable lithium-sulfur batteries: Progress and prospects[J]. Energy Storage Materials,2015,1:127-145. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2015.09.008 [5] Zhang J, Cao D, Wu Y, Cheng X, et al. Phase transformation and sulfur vacancy modulation of 2D layered tin sulfide nanoplates as highly durable anodes for pseudocapacitive lithium storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,392:123722. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123722 [6] Wang Y, Huang X, Zhang S, et al. Sulfur hosts against the shuttle effect[J]. Small Methods,2017,2:1700345. [7] Zhuang Z, Kang Q, Wang D, et al. Single-atom catalysis enables long-life, high-energy lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nano Research,2020,13(7):1856-1866. doi: 10.1007/s12274-020-2827-4 [8] Peng H J, Huang J Q, Cheng X B, et al. Review on high-loading and high-energy lithium–sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials,2017,7:1700260. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201700260 [9] Yin Y X, Xin S, Guo Y G, et al. Lithium–sulfur batteries: Electrochemistry, materials and prospects[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2013,52:13186-13200. doi: 10.1002/anie.201304762 [10] Ji X L, Lee K T, Nazar L F, et al. A highly ordered nanostructured carbon–sulphur cathode for lithium–sulphur batteries[J]. Nature Materials,2009,8:500-506. doi: 10.1038/nmat2460 [11] Zhang C, Lin Y, Zhu Y, et al. Improved lithium-ion and electrically conductive sulfur cathode for all-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. RSC Advances,2017,7:19231-19236. doi: 10.1039/C7RA02174G [12] Ma X Z, Jin B, Xin P M, et al. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes-sulfur composites with enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium/sulfur batteries[J]. Applied Surface Science,2014,307:346-350. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.04.036 [13] Chen L, Yu H, Li W, et al. Interlayer design based on carbon materials for lithium-sulfur batteries: A review[J]. J Mater Chem. A,2020,8:10709. doi: 10.1039/D0TA03028G [14] Guo X, Zheng S, Zhang G, et al. Nanostructured graphene-based materials for flexible energy storage[J]. Energy Storage Materials,2017,9:150-169. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2017.07.006 [15] LIN J L, SU S M, HE Y B, et al. Synthesis and development of graphene-inorganic semiconductor nanocomposites[J]. Chemical Reviews,2015,115:8294-8343. doi: 10.1021/cr400607y [16] Chen K, Wang Q, Niu Z, et al. Graphene-based materials for flexible energy storage devices[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry,2018,27:12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2017.08.015 [17] Luo S W, Yao M J, Lei S, et al. Freestanding reduced graphene oxide-sulfur composite films for highly stable lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nanoscale,2017,9:4646-4651. doi: 10.1039/C7NR00999B [18] Jin J, Wen Z Y, Ma G Q, et al. Flexible self-supporting graphene–sulfur paper for lithium sulfur batteries[J]. RSC Advances,2013,3:2558-2560. doi: 10.1039/c2ra22808d [19] Sun C S, Guo D C, Shao Q J, et al. Preparation of gelatin-derived nitrogen-doped large pore volume porous carbons as sulfur hosts for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. New carbon materials,2021,36(1):198-208. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5805(21)60014-8 [20] Jayaprakash N, Shen J, Moganty S S, et al. Porous hollow carbon@sulfur composites for high-power lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2011,50:5904-5908. doi: 10.1002/anie.201100637 [21] Mukkabla R, Meduri P, Deepa M, et al. Durable Li-S batteries with nanosulfur/graphite nanoplatelets composites[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2016,303:369-383. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.146 [22] Liang C D, Dudney N J, Howe J Y. Hierarchically structured sulfur/carbon nanocomposite material for high-energy lithium battery[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2009,21:4724-4730. doi: 10.1021/cm902050j [23] Carter R, Ejorh D, Share K, et al. Surface oxidized mesoporous carbons derived from porous silicon as dual polysulfide confinement and anchoring cathodes in lithium sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2016,330:70-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.08.128 [24] Wang D W, Li F, Liu M, et al. 3D aperiodic hierarchical porous graphitic carbon material for high-rate electrochemical capacitive energy storage[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2008,47:373-376. doi: 10.1002/anie.200702721 [25] Yu M P, Ma J S, Song H Q, et al. Atomic layer deposited TiO2 on a nitrogen-doped graphene/sulfur electrode for high performance lithium–sulfur batteries[J]. Energy Environmental Science,2016,9:1495-1503. doi: 10.1039/C5EE03902A [26] Zhang Y, Guo Y, Wang B Y, et al. An integrated hybrid interlayer for polysulfides/selenides regulation toward advanced Li-SeS2 batteries[J]. Carbon,2020,161:413-422. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.01.102 [27] Li H, Sun M Q, Zhang T, et al. Improving the performance of PEDOT-PSS coated sulfur@activated porous graphene composite cathodes for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2014,2:18345-18352. doi: 10.1039/C4TA03366C [28] Zhou G M, Li L, Ma C Q, et al. A graphene foam electrode with high sulfur loading for flexible and high energy Li-S batteries[J]. Nano Energy,2015,11:356-365. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2014.11.025 [29] Sun M Q, Li H, Wang J, et al. Promising graphene/carbon nanotube foam@p-conjugated polymer self-supporting composite cathodes for high-performance rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Carbon,2015,94:864-871. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.07.054 [30] Deng N P, Kang W M, Liu Y B, et al. A review on separators for lithium-sulfur battery: Progress and prospects[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2016,331:132-155. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.09.044 [31] Wang Q S, Wen Z Y, Yang J H, et al. Electronic and ionic co-conductive coating on the separator towards high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2016,306:347-353. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.11.109 [32] Zhu J D, Yanilmaz M, Fu K, et al. Understanding glass fiber membrane used as a novel separator for lithium–sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2016,504:89-96. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2016.01.020 [33] Zeng Q C, Leng X, Wu K H, et al. Electroactive cellulose-supported graphene oxide interlayers for Li-S batteries[J]. Carbon,2015,93:611-619. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.05.095 [34] Huang J Q, Xu Z L, Abouali S, et al. Porous graphene oxide/carbon nanotube hybrid films as interlayer for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Carbon,2016,99:624-632. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.12.081 [35] Zhang Z A, Wang G C, Y Q, et al. A freestanding hollow carbon nanofiber/ reduced graphene oxide interlayer for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal Alloys and Compounds,2016,663:501-506. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.11.120 [36] Zhang Y, Xiang M, Wu H, et al. Interwoven V2O5 nanowire/graphene nanoscroll hybrid assembled as efficient polysulfide-trapping-conversion interlayer for long-life lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2018,6:19358-19370. doi: 10.1039/C8TA06610H [37] Zhang Z Y, Lai Y Q, Zhang Z A, et al. A functional carbon layer-coated separator for high performance lithium sulfur batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics,2015,278:166-171. doi: 10.1016/j.ssi.2015.06.018 [38] Sun L, Li H, Zhao M, Wang G. High-performance lithium-sulfur batteries based on self-supporting graphene/carbon nanotube foam@sulfur composite cathode and quasi-solid-state polymer electrolyte[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,332:8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.075 [39] Zhou G M, Li L, Wang D W, et al. A flexible sulfur-graphene-polypropylene separator integrated electrode for advanced Li-S batteries[J]. Advanced Materials,2015,27:641-647. doi: 10.1002/adma.201404210 [40] Alhajji E M, Wang W X, Zhang W L, et al. A hierarchical three-dimensional porous laser-scribed graphene film for suppressing polysulfide shuttling in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12:18833-18839. [41] Li L, Chen C, Yu A. New electrochemical energy storage systems based on metallic lithium anode—the research status, problems and challenges of lithium-sulfur, lithium-oxygen and all solid state batteries[J]. Science China Chemistry,2017,60(11):1402-1412. doi: 10.1007/s11426-017-9041-1 [42] Zhang Q, Ding Z, Liu G, Wan H, et al. Molybdenum trisulfide based anionic redox driven chemistry enabling high-performance all-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials,2019,23:168-180. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2019.05.015 [43] Lei D, Shi K, Ye H, et al. Progress and perspective of solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2018,28:1707570. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201707570 [44] Wang Z, Xu X, Ji S M, et al. Recent progress of flexible sulfur cathode based on carbon host for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2020,55:56-72. [45] Wang X, Shi G. Flexible graphene devices related to energy conversion and storage[J]. Energy Environmental Science,2015,8:790-823. doi: 10.1039/C4EE03685A [46] Huang X, Sun B, Li K, et al. Mesoporous graphene paper immobilized sulfur as a flexible electrode for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A,2013,1:13484-13489. [47] Wan H, Cai L, Han F, et al. Construction of 3D electronic/Ionic conduction networks for all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Small,2019,15:1905849. doi: 10.1002/smll.201905849 [48] Ulissi U, Ito S, Hosseini S M, et al. High capacity all-solid-state lithium batteries enabled by pyrite-sulfur composites[J]. Advanced Energy Materials,2018,8(26):1801462. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201801462 [49] Tanibata N, Matsuyama T, Hayashi A, et al. All-solid-state sodium batteries using amorphous TiS3 electrode with high capacity[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2015,275:284-287. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.10.193 [50] Zhang Q, Wan H, Liu G, et al. Rational design of multi-channel continuous electronic/ionic conductive networks for room temperature vanadium tetrasulfide-based all-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nano Energy,2019,57:771-782. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.01.004 [51] Xu R, Wu Z, Zhang S, et al. Construction of all-solid-state batteries based on a sulfur-graphene composite and Li9.54Si1.74P1.44S11.7Cl0.3 solid electrolyte[J]. Chemisgtry-European Journal,2017,23:13950-13956. doi: 10.1002/chem.201703116 [52] Yao X, Huang N, Han F, Zhang Q, et al. High-performance all-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries enabled by amorphous sulfur-coated reduced graphene oxide cathodes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials,2017,7:1602923. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201602923 [53] Kong L, Li B Q, Peng H J, et al. Porphyrin-derived graphene-based nanosheets enabling strong polysulfide chemisorption and rapid kinetics in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials,2018,8:1800849. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201800849 [54] Li H, Sun L, Zhang Y, et al. Enhanced cycle performance of Li/S battery with the reduced graphene oxide/activated carbon functional interlayer[J]. Journal Energy Chemistry,2017,26:1276-1281. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2017.09.009 [55] Peng H J, Wang D W, Huang J Q, et al. Janus separator of polypropylene-supported cellular graphene framework for sulfur cathodes with high utilization in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Science,2016,3:1500268. doi: 10.1002/advs.201500268 [56] Chen H, Xiao Y, Chen C, et al. Conductive MOF-modified separator for mitigating the shuttle effect of lithium-sulfur battery through a filtration method[J]. ACS Applied Materials &g Interfaces,2019,11:11459-11465. [57] Chen X, Hu S, Liu Y, et al. Membrane and electrode engineering of high-performance lithium sulfur batteries modified by stereotaxically-constructed graphene[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,834:155096. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155096 [58] Do ng, Q, WANG T, Gan R Y. Balancing the seesaw: Investigation of a separator to grasp polysulfides with diatomic chemisorption[J]. ACS Applied Materials &g Interfaces,2020,12:20596-20604. [59] Du Z, Guo C, Wang L, et al. Atom-thick interlayer made of CVD-grown graphene, film on separator for advanced lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9:43696-43703. [60] Cengiz E C, Salihoglu O, Ozturk O, et al. Ultra-lightweight chemical vapor deposition grown multilayered graphene coatings on paper separator as interlayer in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,777:1017-1024. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.11.071 [61] Zhang Y, Wang R, Tang W, et al. Efficient polysulfide barrier of a graphene aerogel-carbon nanofibers-Ni network for high-energy density lithium–sulfur batteries with ultrahigh sulfur content[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2018,6:20926-20938. doi: 10.1039/C8TA08048H [62] Yuan Z, Peng H J, Hou T Z, et al. Powering lithium-sulfur battery performance by propelling polysulfide redox at sulfiphilic hosts[J]. Nano Letter,2016,16:519-527. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04166 [63] Gou J, Zhang H Z, Yang X F, et al. Quasi-stable electroless Ni-P deposition: A pivotal strategy to create flexible Li-S pouch batteries with bench mark cycle stability and specific capacity[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2018,28:1707272. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201707272 [64] Deng D R, Xue F, Jia Y J, et al. Co4N nanosheet assembled mesoporous sphere as a matrix for ultrahigh sulfur content lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Nano,2017,11:6031-6039. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b01945 [65] Li S Y, Wang W P, Duan H, et al. Recent progress on confinement of polysulfides through physical and chemical methods[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry,2018,27:1555-1565. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2018.04.014 [66] Zhang Z W, Peng H J, Zhao M, et al. Heterogeneous/homogeneous mediators for high-energy-density lithium-sulfur batteries: Progress and prospects[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2018,28:1707536. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201707536 [67] Balach J, Singh H K, Gomoll S, et al. Synergistically enhanced polysulfide chemisorption using a flexible hybrid separator with N and S dual-doped mesoporous carbon coating for advanced lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8:14586-14595. [68] Yin L C, Liang J, Zhou G M, et al. Understanding the interactions between lithium polysulfides and N-doped graphene using density functional theory calculations[J]. Nano Energy,2016,25:203-210. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.04.053 [69] Pang Q, Tang J, Huang H, et al. A nitrogen and sulfur dual-doped carbon derived from polyrhodanine@cellulose for advanced lithium−sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Materials,2015,27:6021-6028. doi: 10.1002/adma.201502467 [70] Yi G S, Sim E S, Chung Y C. Effect of lithium-trapping on nitrogen-doped graphene as an anchoring material for lithium-sulfur batteries: A density functional theory study[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2017,19:28189-28194. doi: 10.1039/C7CP04507G [71] Liu C Y, Li EY. Adsorption mechanisms of lithium polysulfides on graphene-based interlayers in lithium sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials,2018,1:455-463. [72] Zhu J, Chen C, Lu Y, et al. Highly porous polyacrylonitrile/graphene oxide membrane separator exhibiting excellent anti-self-discharge feature for high performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Carbon,2016,101:272-280. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.02.007 [73] Chen F, Ma L, Ren J, et al. Sandwich-type nitrogen and sulfur codoped graphene-backboned porous carbon coated separator for high performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nanomaterials,2018,8:191. doi: 10.3390/nano8040191 [74] Liu G, Zhang Z, Tian W, et al. Ni12P5 nanoparticles bound on graphene sheets for advanced lithium–sulfur batteries[J]. Nanoscale,2020,12:10760-10770. doi: 10.1039/C9NR10680D [75] Shi H, Sun Z, Lv W, et al. Efficient polysulfide blocker from conductive niobium nitride@graphene for Li-S batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry,2020,45:135-141. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2019.10.018 [76] Rana M, He Q, Luo B, et al. Multifunctional effects of sulfonyl-anchored, dual-doped multilayered graphene for high areal capacity lithium sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Central Science,2019,5:1946-1958. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.9b01005 [77] Sun K, Guo P, Shang X, et al. Mesoporous boron carbon nitride/graphene modified separators as efficient polysulfides barrier for highly stable lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry,2019,842:34-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.04.047 [78] Zhang L, Wan F, Wang X, et al. Dual-functional graphene carbon as polysulfide trapper for high-performance lithium sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10:5594-5602. [79] Zhang L, Liu D, Muhammad Z, et al. Single nickel atoms on nitrogen-doped graphene enabling enhanced kinetics of lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Materials,2019,31:1903955. doi: 10.1002/adma.201903955 [80] Zuo X T, Zhen M M, Wang C. Ni@N-doped graphene nanosheets and CNTs hybrids modified separator as efficient polysulfide barrier for high-performance lithium sulfur batteries[J]. Nano Research,2019,12:529-536. [81] Gao F, Yan X, Wei Z, et al. Graphene/carbon nanotubes composite as a polysulfide trap for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science,2019,14:3301-3314. [82] Kumar G G, Chung S H, Kumar T R, et al. Three-dimensional graphene−carbon nanotube−Ni hierarchical architecture as a polysulfide trap for lithium−sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10:20627-20634. [83] Song X, Wang S, Chen G, et al. Fe-N-doped carbon nanofiber and graphene modified separator for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,333:564-571. [84] Wu H, Huang Y, Zhang W, et al. Lock of sulfur with carbon black and a three-dimensional graphene@carbon nanotubes coated separator for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Alloy Compounds,2015,708:743-750. [85] Zhang Y, Ge X, Kang Q, et al. Vanadium oxide nanorods embed in porous graphene aerogel as high efficiency polysulfide-trapping-conversion mediator for high performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,393:124570. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124570 [86] Sun Z, Guo Y, Li B, et al. ZnO/carbon nanotube/reduced graphene oxide composite film as an effective interlayer for lithium/sulfur batteries[J]. Solid State Sciences,2019,95:105924. doi: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2019.06.013 [87] Shi N, Xi B, Feng Z, et al. Insight into different-microstructured ZnO/graphene-functionalized separators affecting the performance of lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2019,7:4009-4018. doi: 10.1039/C8TA12409D [88] Wang S, Gao F, Ma R, et al. ZnO Nanoparticles anchored on a N-doped graphene-coated separator for high performance lithium/sulfur batteries[J]. Metals,2018,8:755-766. doi: 10.3390/met8100755 [89] Liu Y, Qin X, Zhang S, et al. Fe3O4-decorated porous graphene interlayer for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10:26264-26273. [90] Hwang J Y, Kim H M, Shin S, et al. Designing a high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries based on layered double hydroxides-carbon nanotubes composite cathode and a dual-functional graphene-polypropylene–Al2O3 separator[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2018,28:1704294. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201704294 [91] Wei N, Cai J, Wang R, et al. Elevated polysulfide regulation by an ultralight all-CVD-built ReS2@N-Doped graphene heterostructure interlayer for lithium–sulfur batteries[J]. Nano Energy,2019,66:104190. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104190 [92] Zhou X, Luo X, Wang H, et al. Reduced graphene oxide@CoSe2 interlayer as anchor of polysulfides for high properties of lithium–sulfur battery[J]. Journals of Materials Science,2019,54:9622-9631. doi: 10.1007/s10853-019-03571-z [93] Qin J, Li B, Huang J, et al. Graphene-based Fe-coordinated framework porphyrin as an interlayer for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers,2019,3:615-619. doi: 10.1039/C8QM00645H [94] Kiai M S, Eroglu O, Kizil H. Polycarboxylate functionalized graphene/S composite cathodes and modified cathode-facing side coated separators for advanced lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nanoscale Research Letters,2019,14:265-276. doi: 10.1186/s11671-019-3099-3 [95] Qu L, Liu P, Zhang P, et al. Carbon-nanotube/sulfur cathode with in-situ assembled Si3N4/ graphene interlayer for high-rate and long cycling-life lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2019,296:155-164. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.11.040 [96] Lei T, Chen W, Lv W, et al. Inhibiting polysulfide shuttling with a graphene composite separator for highly robust lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Joule,2018,2:2091-2104. doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2018.07.022 [97] Zheng Y, Fan H, Li H, et al. Bifunctional separator coated by hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene/rGO for enhanced performance of Li−S batteries: Investigated experimentally and theoretically[J]. Chemistry European Journal,2018,24:13582-13588. doi: 10.1002/chem.201802386 [98] Kim P J, Narayanan S, Xue J, et al. Li-ion-permeable and electronically conductive membrane comprising garnet-type Li6La3Ta1.5Y0.5O12 and graphene toward ultrastable and high-rate lithium sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,1:3733-3741. [99] Zhao Y, Liu M, Lv W, et al. Dense coating of Li4Ti5O12 and graphene mixture on the separator to produce long cycle life of lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Nano Energy,2016,30:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.09.030 [100] Zhuang T Z, Huang J Q, Peng H J, et al. Rational integration of polypropylene/graphene oxide/nafion as ternary-layered separator to retard the shuttle of polysulfi des for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Small,2016,12:289-381. [101] Liu P, Qu L, Tian X, et al. Ti3C2Tx/graphene oxide free-standing membranes as modified separators for lithium−sulfur batteries with enhanced rate performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,3:2708-2718. [102] Huang J Q, Zhuang T Z, Zhang Q, et al. Permselective graphene oxide membrane for highly stable and anti-self-discharge lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. ACS Nano,2015,9:3002-3011. doi: 10.1021/nn507178a [103] Bai S, Liu X, Zhu K, et al. Metal−organic framework-based separator for lithium−Sulfur batteries[J]. Nature Energy,2016,1:16094. doi: 10.1038/nenergy.2016.94 [104] Xiao Z, Yang Z, Wang L, et al. A lightweight TiO2/graphene interlayer, applied as a highly effective polysulfide absorbent for fast, long-life lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Materials,2015,27:2891-2900. doi: 10.1002/adma.201405637 -






 下载:
下载: