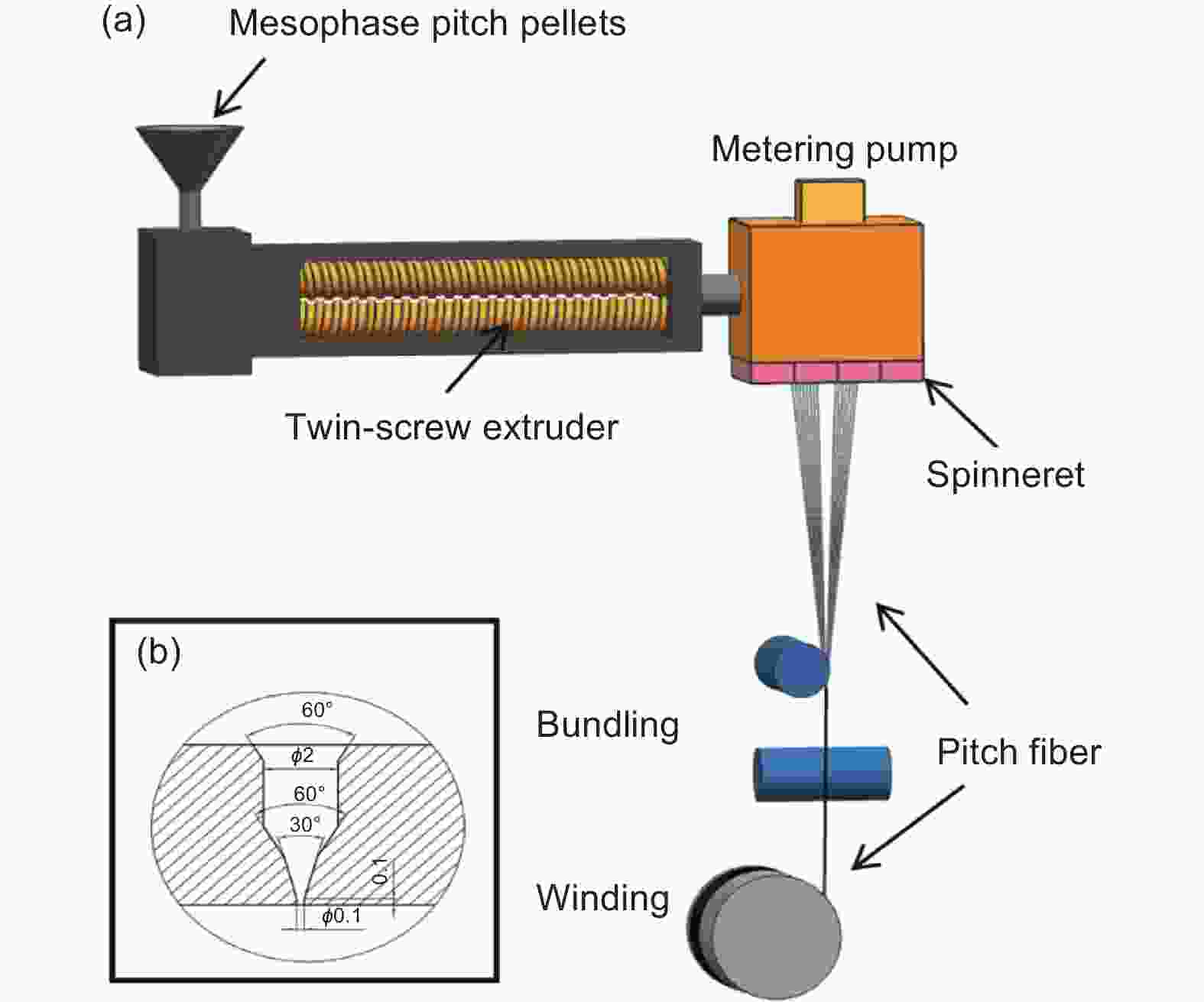
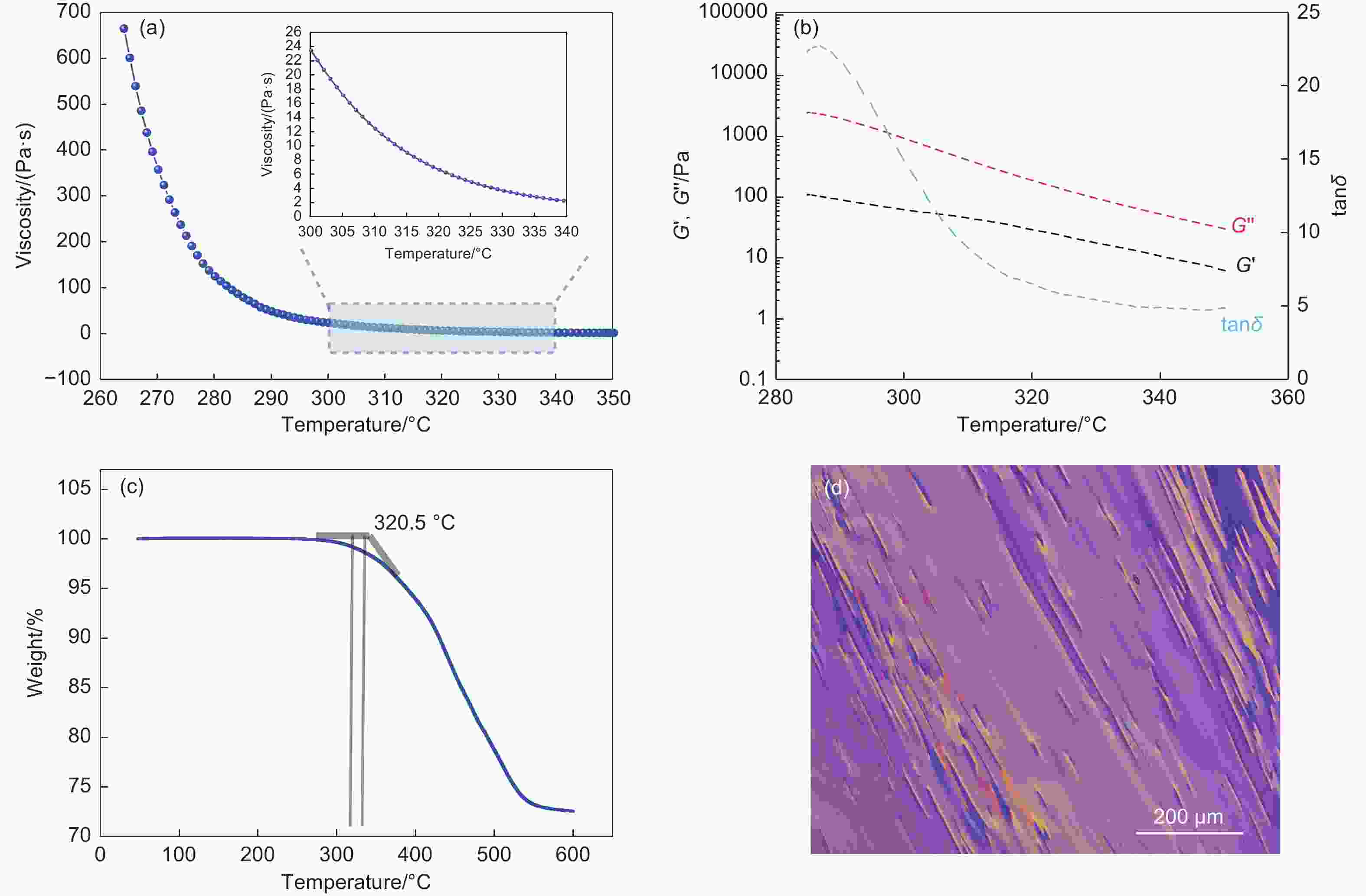
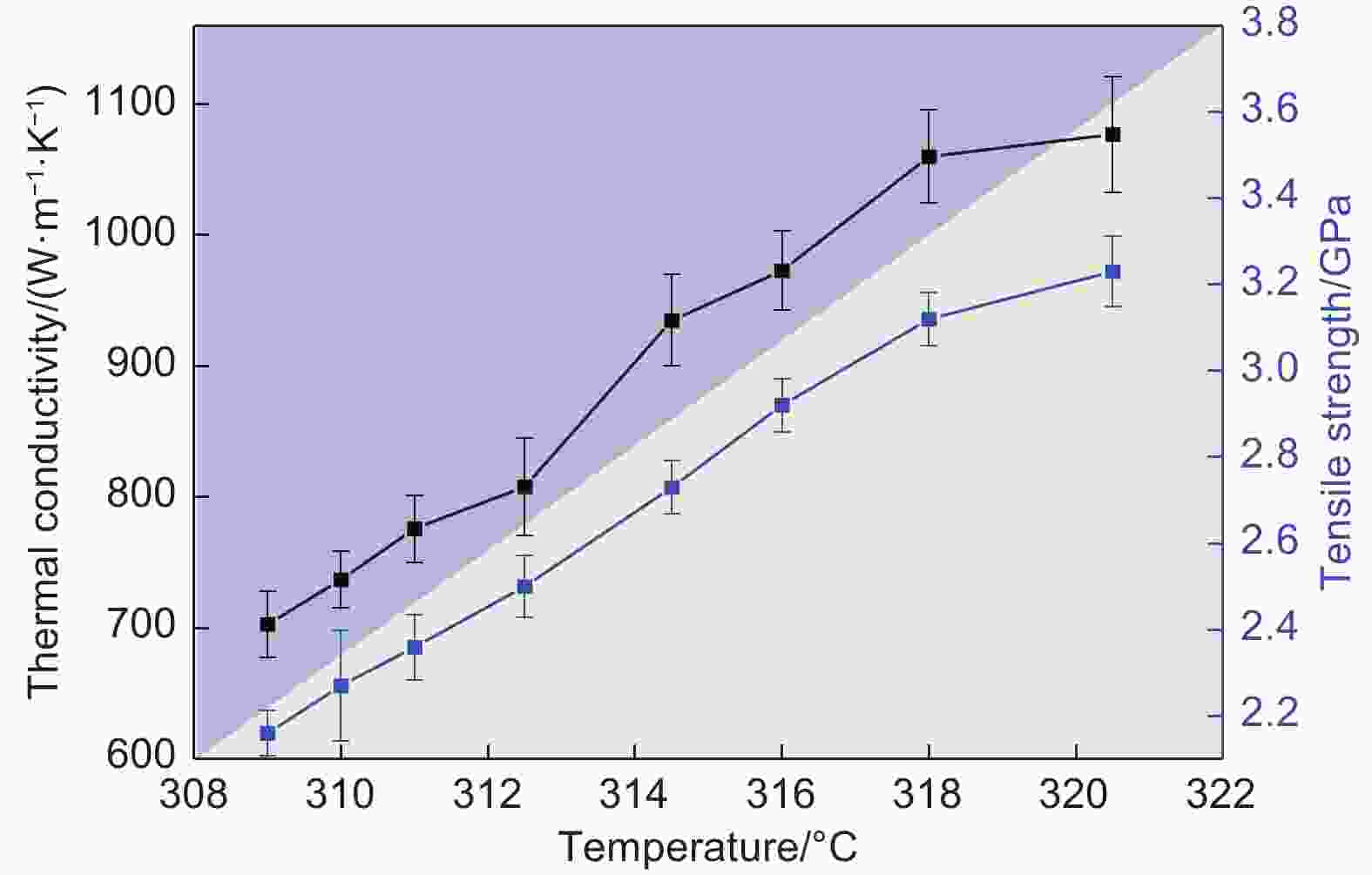
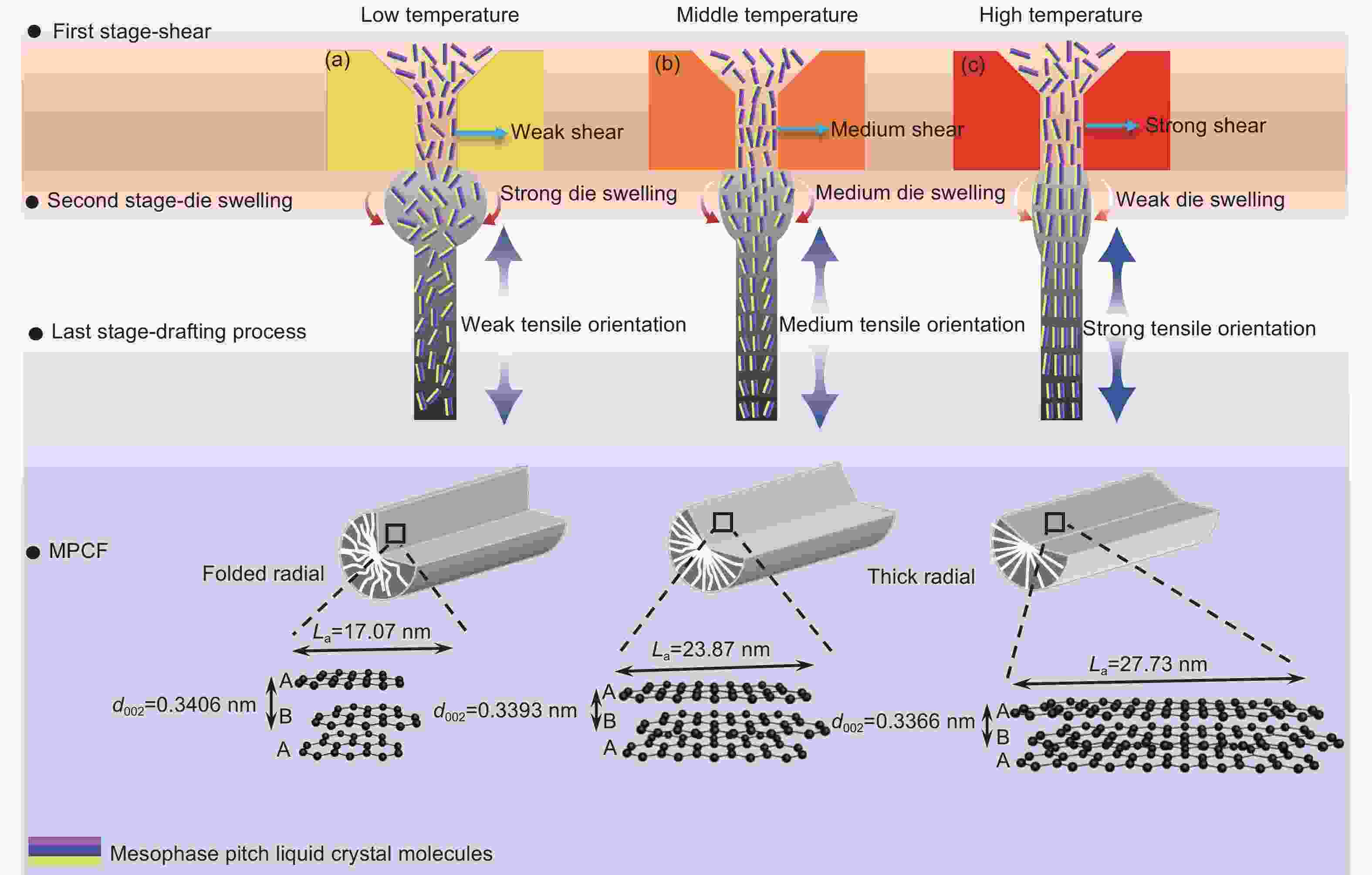
Improving the mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of mesophase-pitch-based carbon fibers by controlling the temperature in industrial spinning equipment
-
摘要: 基于工程化设备,在恒定挤出量条件下,通过调控纺丝温度制备了中间相沥青炭纤维( MPCFs ),探究纺丝温度对MPCFs微观结构、力学和导热性能的影响。结果表明:随着纺丝温度由309升高至320 °C,MPCFs的微观结构由石墨片层细小的褶皱劈裂辐射状结构逐步向石墨片层粗大的劈裂辐射状结构转变,拉伸强度由2.16增大到3.23 GPa,热导率由704升高到1078 W·m−1·K−1。这主要是因为纺丝温度越高,沥青熔体黏度越小,喷丝口处挤出胀大效应越弱,沥青熔体在喷丝孔流道内形成的微晶取向得以保持,以此制备的炭纤维具有更大的晶体尺寸和更高的微晶取向。Abstract: Mesophase-pitch-based carbon fibers (MPCFs) were prepared using industrial equipment with a constant extrusion rate of pitch while controlling the spinning temperature. The influence of spinning temperature on their microstructures, mechanical properties and thermal conductivities was investigated. SEM images of the fractured surface of MPCFs show that the graphite layers have a radiating structure at all spinning temperatures, but change from the fine-and-folded to the large-and-flat morphology when increasing the spinning temperature from 309 to 320 oC . At the same time the thermal conductivity and tensile strength of the MPCFs respectively increase from 704 W·m−1·K−1 and 2.16 GPa at 309 oC to 1 078 W·m−1·K−1 and 3.23 GPa at 320 oC. The lower viscosity and the weaker die-swell effect of mesophase pitch at the outlets of the spinnerets at the higher spinning temperature contribute to the improved orientation of mesophase pitch molecules in the pitch fibers, which improves the crystallite size and orientation of the MPCFs.
-
Key words:
- Mesophase pitch /
- Spinning temperature /
- Carbon fiber /
- High thermal conductivity /
- Mechanical properties
-
Table 1. The basic properties of mesophase pitch
SP/°C TI/% QI/% Ash content/0.1×10−6 Coking value/% H/C AC/% 286.4 75.8 52.6 19.1 90.7 0.54 100 Note: SP, softening point. TI, toluene insoluble. QI, quinoline insoluble. H/C, mole ratio of hydrogen to carbon atoms. AC, anisotropic content. Table 2. Crystalline parameters of MPFs and MPCFs
Samples d002/nm Lc/nm La/nm Z/(°) MPF-309 0.3433 2.22 0.50 40.64 MPF-310 0.3431 2.25 0.48 39.01 MPF-311 0.3428 2.32 0.52 34.85 MPF-312.5 0.3427 2.50 1.64 35.81 MPF-314 0.3426 2.49 1.84 31.56 MPF-316 0.3424 2.54 1.89 30.18 MPF-318 0.3424 2.59 1.88 29.56 MPF-320.5 0.3423 2.66 1.92 28.71 MPCF-309 0.3406 10.76 17.07 14.42 MPCF-310 0.3409 10.89 22.84 14.23 MPCF-311 0.3404 10.98 22.97 12.58 MPCF-312.5 0.3381 10.99 23.87 11.57 MPCF-314 0.3393 11.47 26.17 11.02 MPCF-316 0.3406 11.53 27.14 10.41 MPCF-318 0.3399 12.08 27.50 9.94 MPCF-320.5 0.3366 13.78 27.73 8.48 Table 3. Microstructure, tensile strength and thermal conductivity of fibers prepared in other studies
Samples Microstructure Tensile strength/GPa Thermal conductivity/(W·m−1·K−1) References Ribbon 3000 °C Ribbon 2.53 ~1150 [26] CM-260 Ribbon / 837 [27] SGF Round 1.07 ± 0.30 / [8] Modified Fiber CB Round / 500 [11] MPCF-3 Round 2.12 1322 [28] XN-90 Round 3.43 500 [29-30] K13C2U Round 3.80 620 [31] K13D2U Round 3.70 800 [32] P120 Split 2.41 640 [29- 33] K1100 Split 3.10 1100 [33, 34] MPCF-320.5 Split 3.23 1077 This work -
[1] Snead L L, Balden M, Causey RA, et al. High thermal conductivity of graphite fiber silicon carbide composites for fusion reactor application[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials,2002,307(2):1200-1204. [2] Wang M, Kang Q, Ning P. Thermal conductivity enhancement of carbon fiber composites[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2009,29(2-3):418-421. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2008.03.004 [3] Li T, Xu Z, Hu Z, et al. Application of a high thermal conductivity C/C composite in a heat-redistribution thermal protection system[J]. Carbon,2010,48(3):924-925. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2009.10.043 [4] Yuan G, Li X, Dong Z, et al. Pitch-based ribbon-shaped carbon-fiber-reinforced one-dimensional carbon/carbon composites with ultrahigh thermal conductivity[J]. Carbon,2014,68(3):413-425. [5] Manocha LM, Warrier A, Manocha S, et al. Thermophysical properties of densified pitch based carbon/carbon materials—I. Unidirectional composites[J]. Carbon,2006,44(3):480-487. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2005.08.012 [6] Qin X, Lu Y, Xiao H, et al. A comparison of the effect of graphitization on microstructures and properties of polyacrylonitrile and mesophase pitch-based carbon fibers[J]. Carbon,2012,50(12):4459-4469. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2012.05.024 [7] Bermudez V, Ogale A A. Adverse effect of mesophase pitch draw-down ratio on carbon fiber strength[J]. Carbon,2020,168:328-336. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.06.062 [8] Sieira P, Mendes P R D S, Castro A D, et al. Impact of spinning conditions on the diameter and tensile properties of mesophase petroleum pitch carbon fibers using design of experiments[J]. Materials Letters,2021,285:129110. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.129110 [9] Wu H, Huang D, Ye C, et al. Engineering microstructure toward split-free mesophase pitch-based carbon fibers[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2022,57(4):2411-2423. doi: 10.1007/s10853-021-06770-9 [10] Xu H, Guo J, Li W, et al. The effect of the molecular structure of naphthalene-based mesophase pitch on the properties of carbon fibers derived from it[J]. New Carbon Materials,2023,38(2):369-375. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5805(23)60709-7 [11] Guo J, Li Z, Li B, et al. Hydrogenation of coal tar pitch for improved mesophase pitch molecular orientation and carbon fiber processing[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis,2023,174:106146. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2023.106146 [12] Cao Y, Zang C, Zhang J, et al. High thermal-conductivity mesophase pitch-based graphite fiber with circular cross-section through a spinneret with a Y-shaped spinning hole[J]. Carbon Trends,2023,10:100244. doi: 10.1016/j.cartre.2022.100244 [13] Yamada Y, Sasaki H. Inventors, laid-open Japanese patent application[P]. JP patent, 59-53717, 1984. [14] White JL, Buechler M. Mesophase mechanisms in the formation of graphitic microstructures[J]. Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society,1984,187(4):25. [15] Mochida I, Yoon S H, Takano N, et al. Microstructure of mesophase pitch-based carbon fiber and its control[J]. Carbon,1996,34(8):941-956. doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(95)00172-7 [16] Mochida I, Yoon S H, Korai Y. Control of transversal texture in circular mesophase pitch-based carbon fibre using non-circular spinning nozzles[J]. Journal of Materials Science,1993,28(9):2331-2336. doi: 10.1007/BF01151662 [17] Yoon S H, Takano N, Korai Y, et al. Crack formation in mesophase pitch-basedcarbon fibres: Part I Some influential factors for crack formation[J]. Journal of Materials Science,1997,32(10):2753-2758. doi: 10.1023/A:1018699711846 [18] Cho T, Lee Y S, Rao R, et al. Structure of carbon fiber obtained from nanotube-reinforced mesophase pitch[J]. Carbon,2003,41(7):1419-1424. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00086-1 [19] Liu Z, Ouyang T, Yang X, et al. Effect of spinning temperature on the structure and properties of mesophase pitch carbon fibers[J]. Carbon,2012(2):18-23. [20] Yao X, Ouyang T, Fei Y, et al. Investigation of effect of spinning conditions on diameter of mesophase pitch-based carbon fiber by taguchi experimental design[J]. New Chemical Materials,2016,44(5):136-138,141. [21] Ogale A A, Lin C, Anderson D P, et al. Orientation and dimensional changes in mesophase pitch-based carbon fibers[J]. Carbon,2002,40(8):1309-1319. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(01)00300-1 [22] Sauder C, Lamon J, Pailler R. The tensile behavior of carbon fibers at high temperatures up to 2400 °C[J]. Carbon,2004,42(4):715-725. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2003.11.020 [23] Zhang X, Fujiwara S, Fujii M. Measurements of thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity of a single carbon fiber[J]. International Journal of Thermophysics,2000,21(4):965-980. doi: 10.1023/A:1006674510648 [24] Qiang Z, Min Z, Mao P, et al. Rheological study of microstructures and properties for polymeric materials[J]. Frontiers of Materials Science in China,2007,1(1):1-6. doi: 10.1007/s11706-007-0001-5 [25] Gahleitner M. Melt rheology of polyolefins[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2001,26(6):895-944. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6700(01)00011-9 [26] Yuan G, Li X, Dong Z, et al. The structure and properties of ribbon-shaped carbon fibers with high orientation[J]. Carbon,2014,68(2):426-439. [27] Ma Z, Shi J, Song Y, et al. Carbon with high thermal conductivity, prepared from ribbon-shaped mesosphase pitch-based fibers[J]. Carbon,2006,44(7):1298-1301. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2006.01.015 [28] Zhang X, Ning S, Ma Z, et al. The structural properties of chemically derived graphene nanosheets/mesophase pitch-based composite carbon fibers with high conductivities[J]. Carbon,2020,156:499-505. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.09.085 [29] Emmerich, Francisco G. Young’s modulus, thermal conductivity, electrical resistivity and coefficient of thermal expansion of mesophase pitch-based carbon fibers[J]. Carbon,2014,79:274-293. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2014.07.068 [30] Liang J, Gu Y, Bai M, et al. Electromagnetic shielding property of carbon fiber felt made of different types of short-chopped carbon fibers[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2019,121:289-298. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.03.037 [31] Whatley B L. Thermal management material, devices and methods therefor[P]. U. S. Patent, 2005-1-18, 6844054. [32] Rauch M P. Thermal characterization and optimization of the pixel module support structure for the phase-1 upgrade of the cms pixel detector[D]. Aachen, Tech. Hochsch, 2015. [33] Minus M, Kumar S. The processing, properties, and structure of carbon fibers[J]. JOM,2005,57(2):52-58. doi: 10.1007/s11837-005-0217-8 [34] Blanco C, Appleyard S P, Rand B. Study of carbon fibres and carbon–carbon composites by scanning thermal microscopy[J]. Journal of Microscopy,2002,205(1):21-32. doi: 10.1046/j.0022-2720.2001.00974.x [35] Kundu S, Ogale A A. Rheostructural studies of a discotic mesophase pitch at processing flow conditions[J]. Rheol Acta,2010,49(8):845-854. doi: 10.1007/s00397-010-0448-7 [36] Zhao J, Ouyang T, Yao X, et al. Die swell behavior of liquid crystalline mesophase pitch[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2016,51(15):7361-7369. doi: 10.1007/s10853-016-0025-2 [37] Huang D, White J L. Experimental and theoretical investigation of extrudate swell of polymer melts from small (length)/(cross-section) ratio slit and capillary dies[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science,1980,20(3):182-189. [38] Liang J Z. Effects of extrusion conditions on die-swell behavior of polypropylene/diatomite composite melts[J]. Polymer Testing,2008,27(8):936-940. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2008.08.001 -






 下载:
下载: