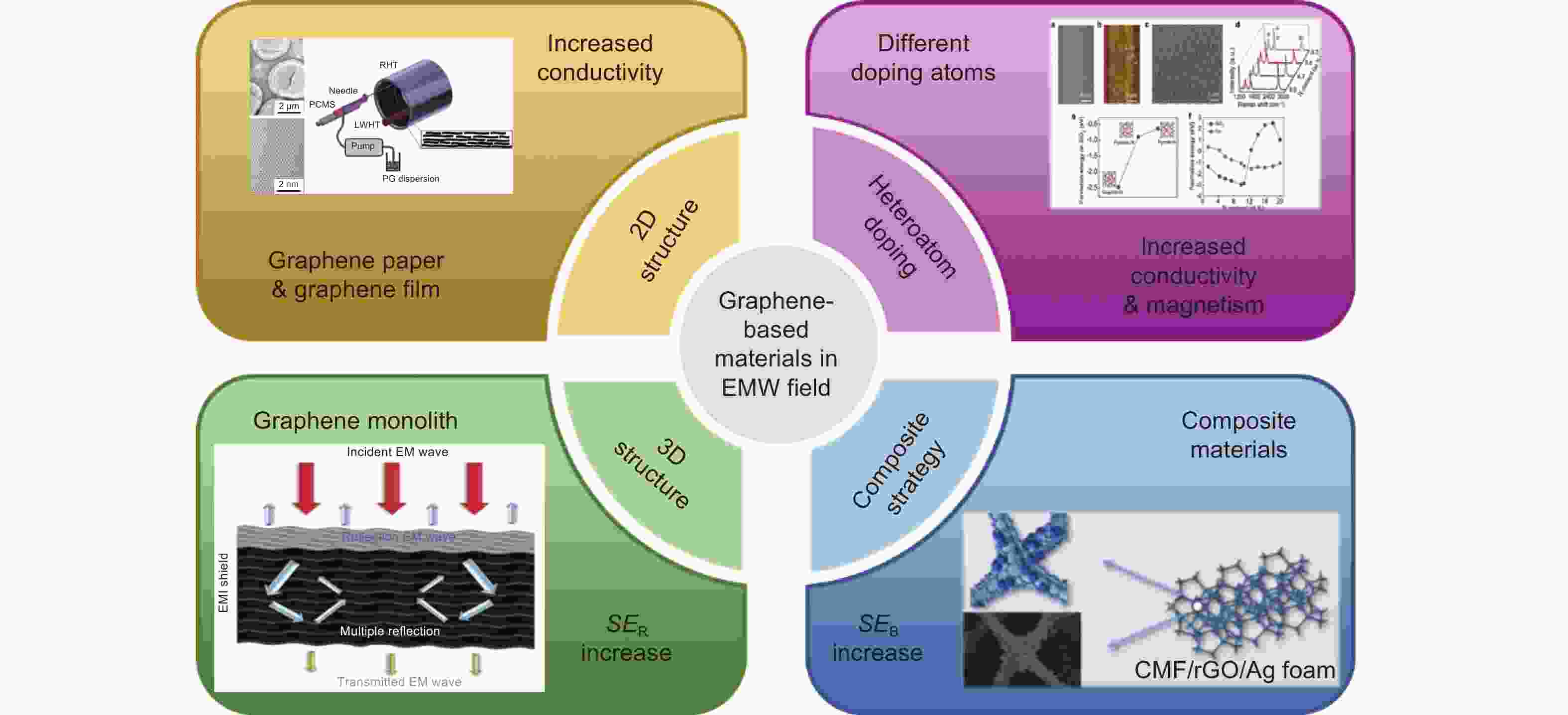
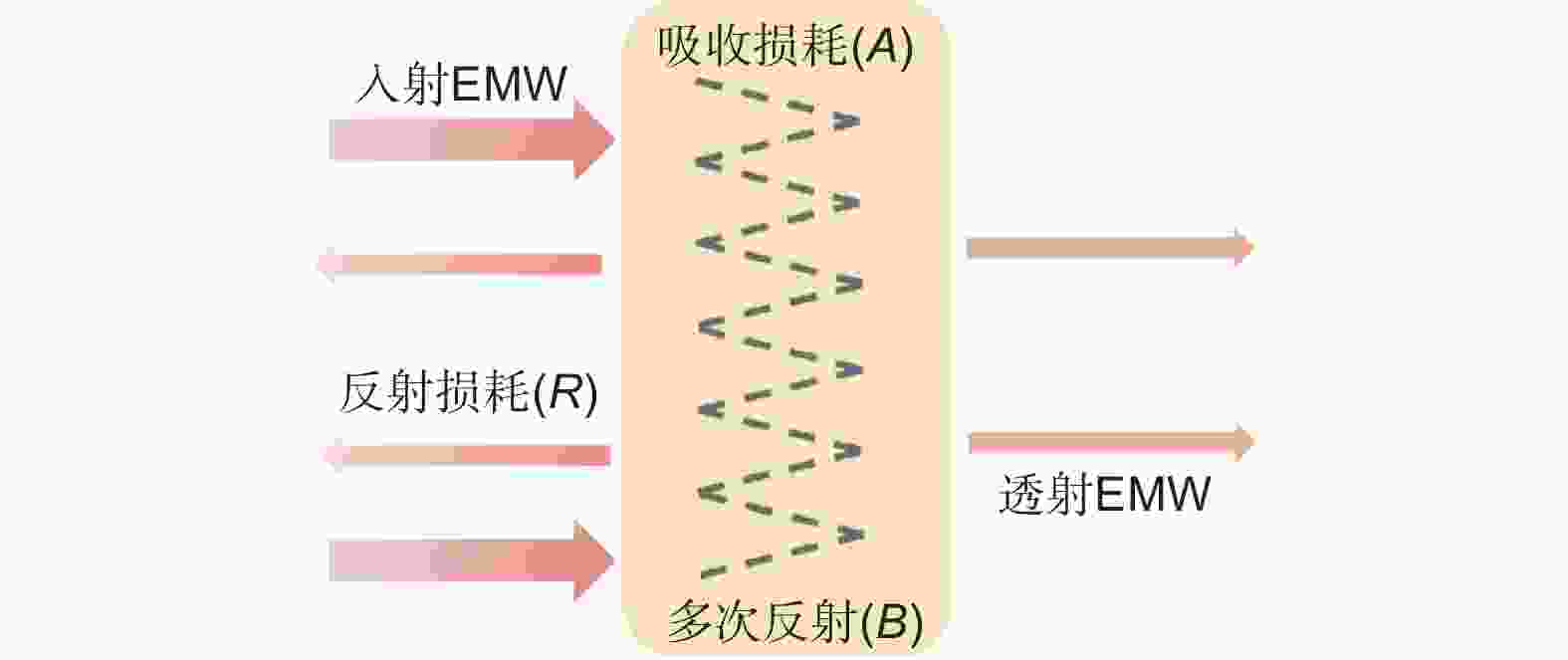
-
摘要:
通信技术在为人类的生活带来便利的同时,其产生的电磁辐射对社会安全、人体健康产生的危害也受到了社会各界的广泛关注,宽屏蔽范围、高吸收效率和高稳定性的电磁屏蔽材料逐渐成为研究热点。石墨烯是一种导电性高、比表面积大且可调控性高的轻质材料,可有效实现电磁衰减,保护精密电子设备和人体健康,在电磁屏蔽领域具有广阔的应用前景。本综述从电磁屏蔽的基本原理与石墨烯基材料的结构特性角度,阐述了石墨烯及其衍生物的电磁屏蔽特点,总结了结构调控以及表面异质化、复合化策略在电磁屏蔽领域的应用。结构调控有利于提高石墨烯基材料对电磁波的吸收损耗和多重反射损耗;表面异质化和复合化策略有利于提高石墨烯基材料的界面极化和磁特性,从而加强对电磁波的吸收损耗和磁损耗。总结了石墨烯基电磁屏蔽材料的改性方法,旨在为开发新一代绿色、轻薄、高屏蔽带宽的电磁屏蔽材料提供启发,指明石墨烯基电磁屏蔽材料的未来发展方向。
Abstract:The development of communication technology has had great benefits but the detrimental effects of electromagnetic radiation have also become important. There has therefore been growing research on electromagnetic shielding materials that have a wide shielding range, high absorption efficiency and stability. Graphene, a lightweight material with an exceptional electrical conductivity and a large specific surface area, has remarkable potential in this application. We first elucidate the fundamental principles of electromagnetic shielding and the structural characteristics of graphene-based materials while highlighting their unique electromagnetic shielding properties. We also provide an overview of common strategies for changing graphene-based materials including structural modification, heteroatom doping, and their incorporation in composite materials to improve this property. Structural modification can increase the losses of electromagnetic waves by absorption and multiple reflection, and heteroatom doping and incorporation in composite materials can increase the losses by interface polarization and magnetic effects. We also summarize various ways of modifying the materials so that they are lightweight and have a high shielding bandwidth.
-
Key words:
- Graphene /
- Electromagnetic shielding /
- Structural regulation /
- Heteroatom doping /
- Composite material
-
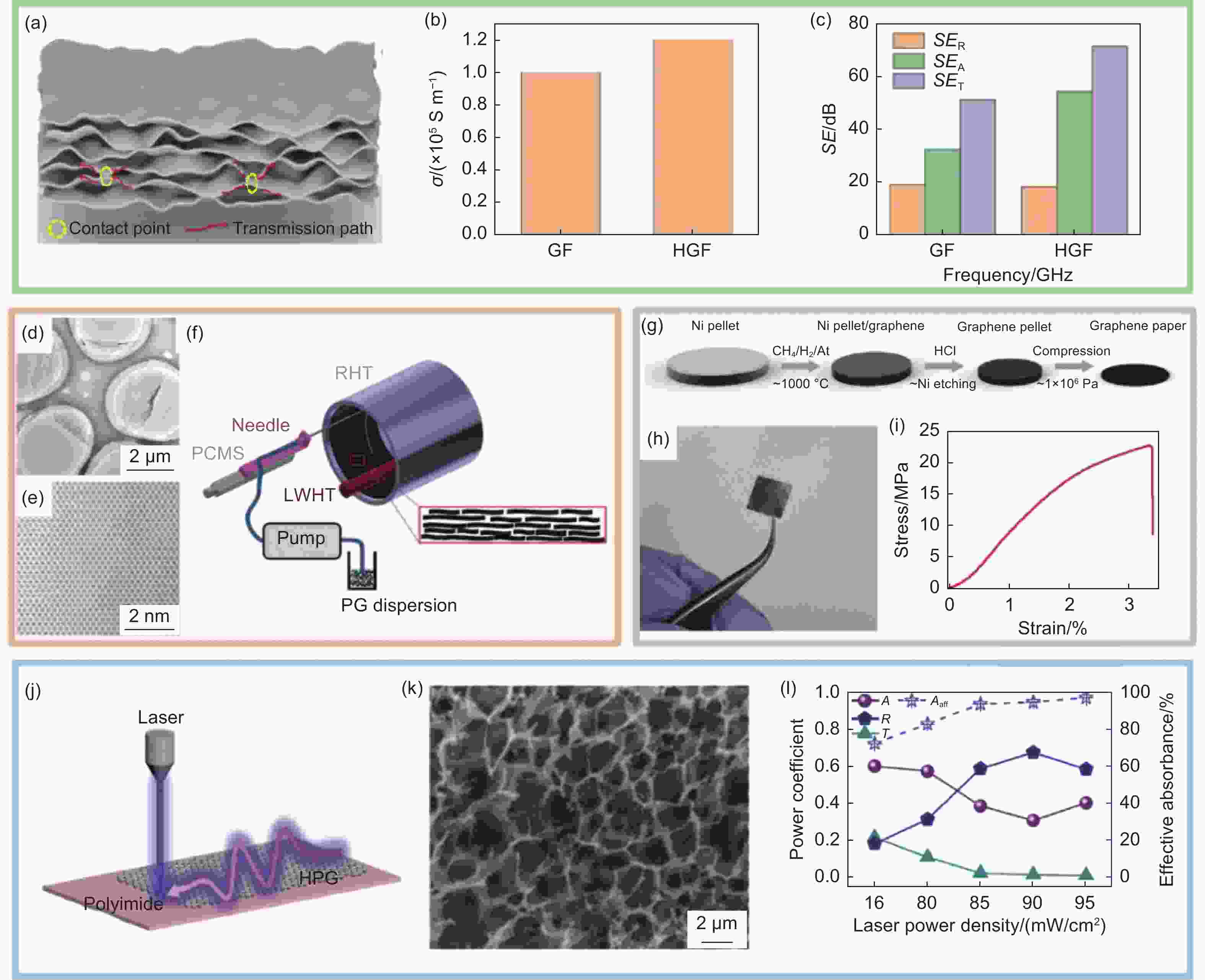
图 3 二维薄膜结构石墨烯基电磁干扰屏蔽材料性能及作用机理:(a)具有丰富接触位点和传输路径的氢碘酸还原石墨烯薄膜(HGF)的导电原理;(b)石墨烯薄膜(GF)和氢碘酸还原石墨烯薄膜(HGF)的电导率;(c)GF和HGF膜的SER、SEA和SET值[37]。石墨烯纳米片的(d)TEM和(e)HRTEM照片;(f)扫描离心铸造法合成石墨烯膜的过程示意图[39]。(g)石墨烯加工成石墨烯纸的示意图;(h)石墨烯薄膜照片;(i)石墨烯纸拉伸应力-应变曲线[40]。(j)多孔石墨烯薄膜(HPG)制备示意图;(k)HPG的SEM照片;(l)在不同激光功率密度(LPD)下HPG在10 GHz下的反射、吸收和透射系数以及有效吸收率[43]
Figure 3. Properties and mechanism of two-dimensional graphene-based EMI shielding materials. (a) The conductivity principle of HGF with rich contact points and transmission paths. (b) Electric conductivity of GF and HGF. (c) SER, SEA, and SET values of GF and HGF films[37]. Typical (d) TEM and (e) HRTEM image of PG nanosheets. (f) Schematic illustration of the synthesis process of PG films by scanning centrifugal casting (SCC) method [39]. (g) Synthesis steps of making graphene pellet and processing it into graphene paper. (h) Photo of graphene paper. (i) Typical tensile stress-strain curve of graphene paper[40]. (j) Schematic diagram of the preparation of the HPG. (k) SEM image of the HPG surface morphology. (l) Reflection, absorption, and transmission coefficients and effective absorbance of the HPG at 10 GHz under different LPDs[43]. Reprinted with permission
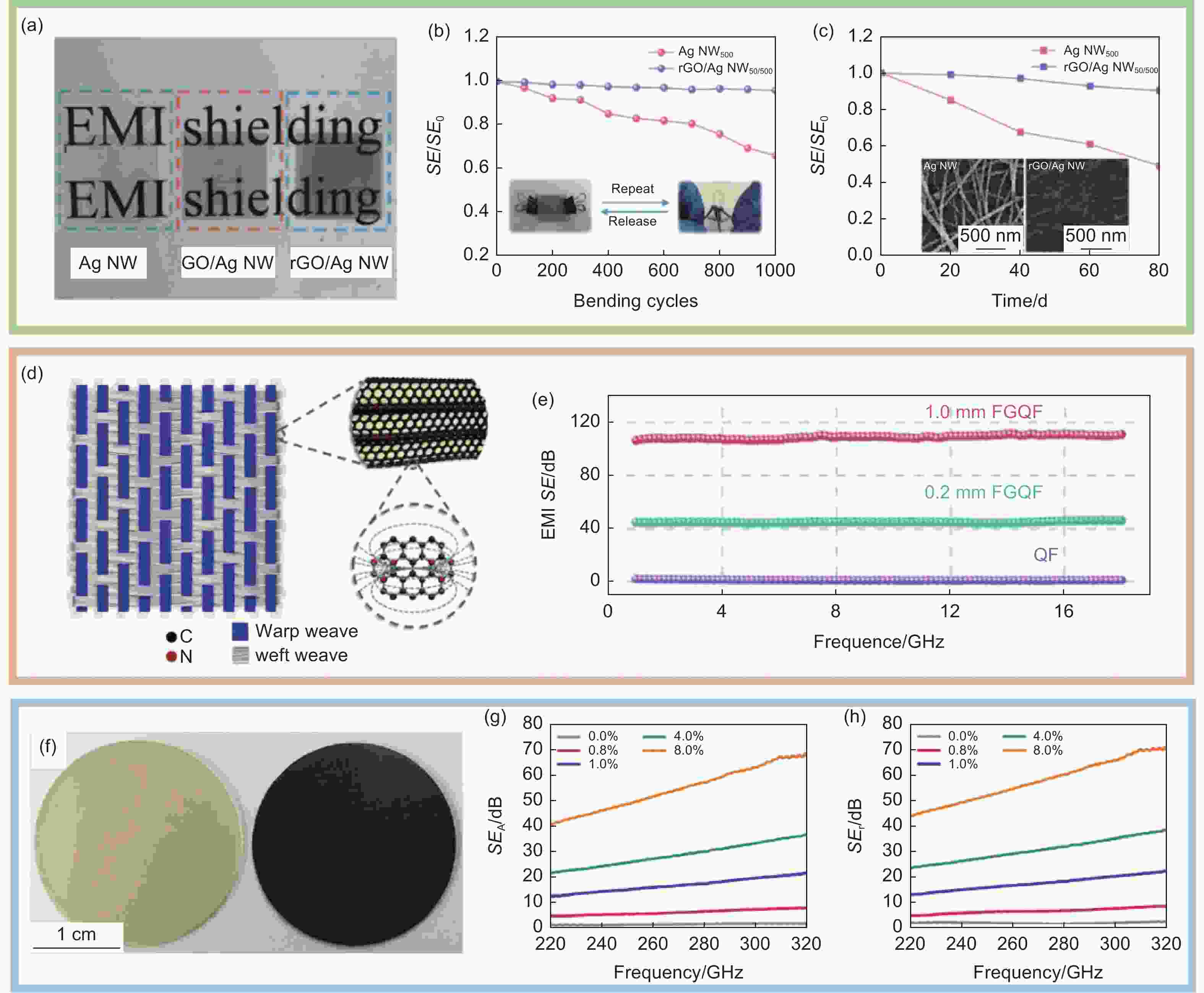
图 4 柔性石墨烯电磁干扰屏蔽器件:(a)银纳米线(Ag NW)修饰的氧化石墨烯(GO/Ag NW)和银纳米线修饰的还原氧化石墨烯(rGO/Ag NW)薄膜;(b)Ag-NW和rGO/Ag NW薄膜在循环弯曲试验过程中的电磁屏蔽效能变化,插图是自制的弯曲测试设备,弯曲半径为2 mm;(c)室温下Ag NW和rGO/Ag NW薄膜长时间暴露在空气中时的EMI SE变化,插图是长时间氧化后Ag NW和rGO/Ag NW膜的SEM图像[45]。(d)铁磁石墨烯石英纤维电磁屏蔽织物(FGQF)示意图;(e)不同厚度的石英织物(QF)和FGQF的电磁屏蔽效能[46]。(f)纯环氧树脂和负载为4%石墨烯的环氧树脂(从左到右);(g)不同石墨烯负载的石墨烯-环氧树脂复合材料的吸收系数;(h)不同石墨烯浓度下的石墨烯-环氧树脂复合材料的SET [49]
Figure 4. Graphene EMI shielding flexible devices: (a) Images of the Ag NW, GO/Ag NW, and rGO/Ag NW films. (b) EMI SE variation in the Ag NW and rGO/Ag NW films during cyclic bending test, the insets are home-made bending test equipment and the bending radius is 2 mm. (c) EMI SE variation in the Ag NW and rGO/Ag NW films during long-time exposure in air at room temperature. Insets are SEM images of the Ag NW and rGO/Ag NW films after long-time oxidation[45]. (d) Schematics of FGQF. (e) EMI SE of QF and FGQF with various thicknesses [46]. (f) Optical image of the pristine epoxy (left) and epoxy with f = 4% graphene (right). (g) Coefficients of absorption for composites with different graphene loading fractions. (h) SET of composites at different graphene concentrations. As the filler loading increases, SER does not grow significantly whereas SEA increases substantially. SET is substantially increased as a result of SEA enhancement[49]. Reprinted with permission
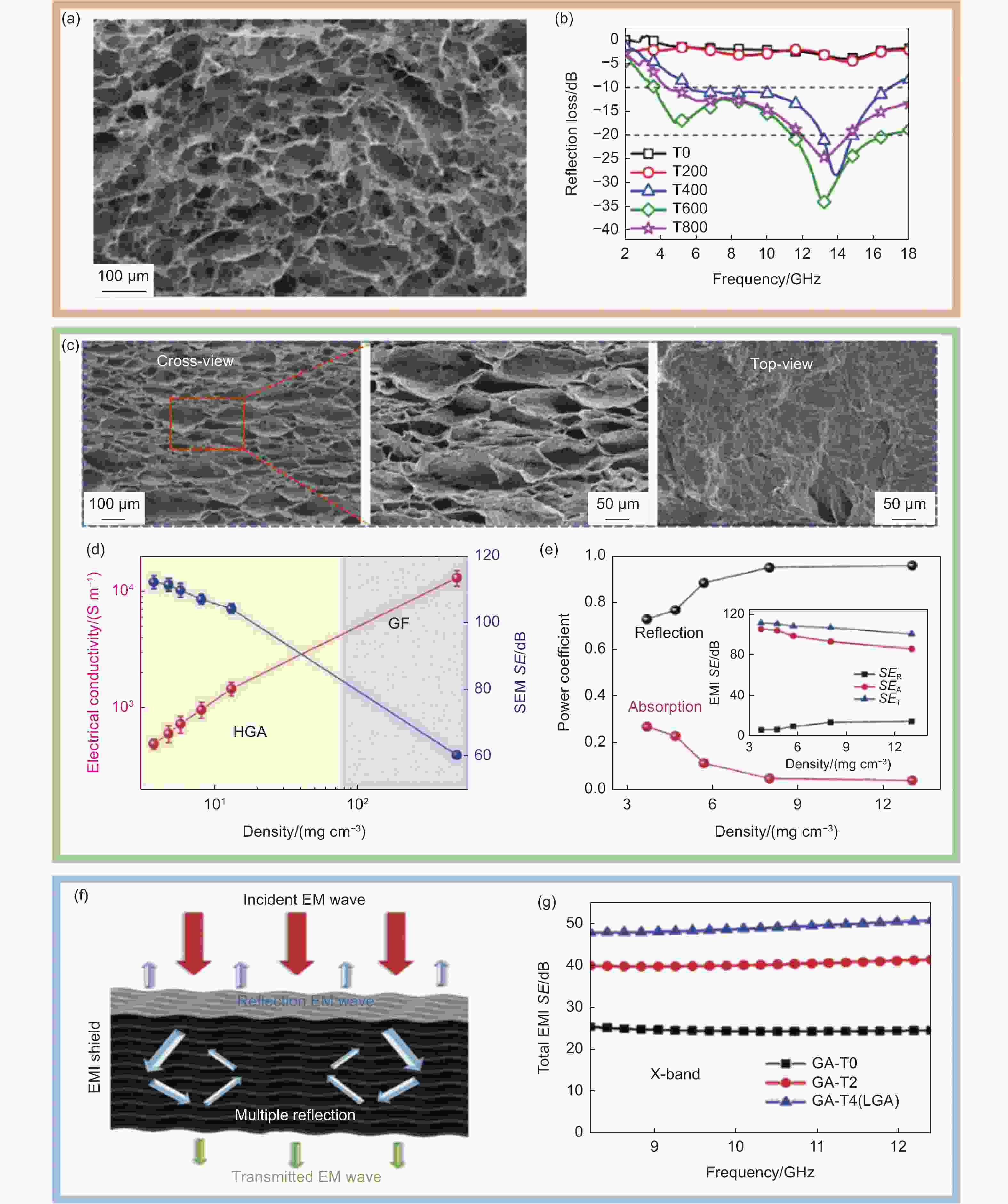
图 5 三维多孔结构石墨烯基电磁干扰屏蔽材料性能及作用机理:(a)石墨烯三维宏观体(GF)的截面SEM图像;(b)不同温度下退火的石墨烯三维宏观体在2~18 GHz下的反射损耗曲线[55]。(c)双曲面石墨烯气凝胶(HGA)的结构表征;(d)石墨烯膜与双曲面石墨烯气凝胶的导电性能对比;(e)不同密度双曲面石墨烯气凝胶的R,A,SER,SEA,SET性能对比[57]。(f)片状石墨烯三维宏观体(LGA)的电磁屏蔽机构示意图;(g)厚度为2 mm的GA-T0、GA-T2和GA-T4(叔丁醇质量分数依次为0%、20%和40%)在X波段的电磁屏蔽效能[58]
Figure 5. Performance and mechanism of three-dimensional porous graphene-based electromagnetic interference shielding material: (a) The cross-sectional SEM images of GF. (b) The reflection loss curves for the GFs by different thermal treatments in 2-18 GHz[55]. (c) Top-view SEM images HGA. (d) Electrical conductivity and EMI SE at the X-band of the graphene film and HGA; (e) R, A, SER, SEA, SET of HGAs with different densities[57]. (f) Schematic diagram of electromagnetic shielding mechanism of the LGA structure. (g) EMI SE in X band of GA-T0, GA-T2 and GA-T4 (the mass fractions of tert-butyl alcohol are 0%, 20% and 40%, respectively) with the thickness of 2 mm[58]. Reprinted with permission
图 6 异质原子掺杂策略及其电磁屏蔽效能:(a)掺杂剂对石墨烯的狄拉克点位置和费米能级的影响,中间、左侧和右侧分别为本征石墨烯、n型掺杂和p型掺杂石墨烯[61]。(b)微波辅助制备B-N共掺杂还原氧化石墨烯(MRG)的方法以及MRG、B-MRG、N-MRG和B-N-MRG的吸收效率[67]。(c)氟掺杂还原氧化石墨烯的合成;(d)rGO160、FrGO100和FrGO160样品的电磁屏蔽效能[68]
Figure 6. Schematic diagram of heteroatom doping strategy and its electromagnetic shielding effectiveness: (a) Schematic diagram of the effect of different dopants on the Dirac point position and Fermi level of graphene, with intrinsic graphene in the middle, n-type doped graphene on the left, and p-type doped graphene on the right[61]. (b) Microwave assisted approach for the preparation of B-N codoped MRG and the absorption efficiency of MRG, B-MRG, N-MRG, and B-N-MRG[67]. (c) Synthesis of fluorine-doped reduced graphene oxide. (d) EMI shielding effectiveness of rGO160, FrGO100 andFrGO160 samples[68]. Reprinted with permission
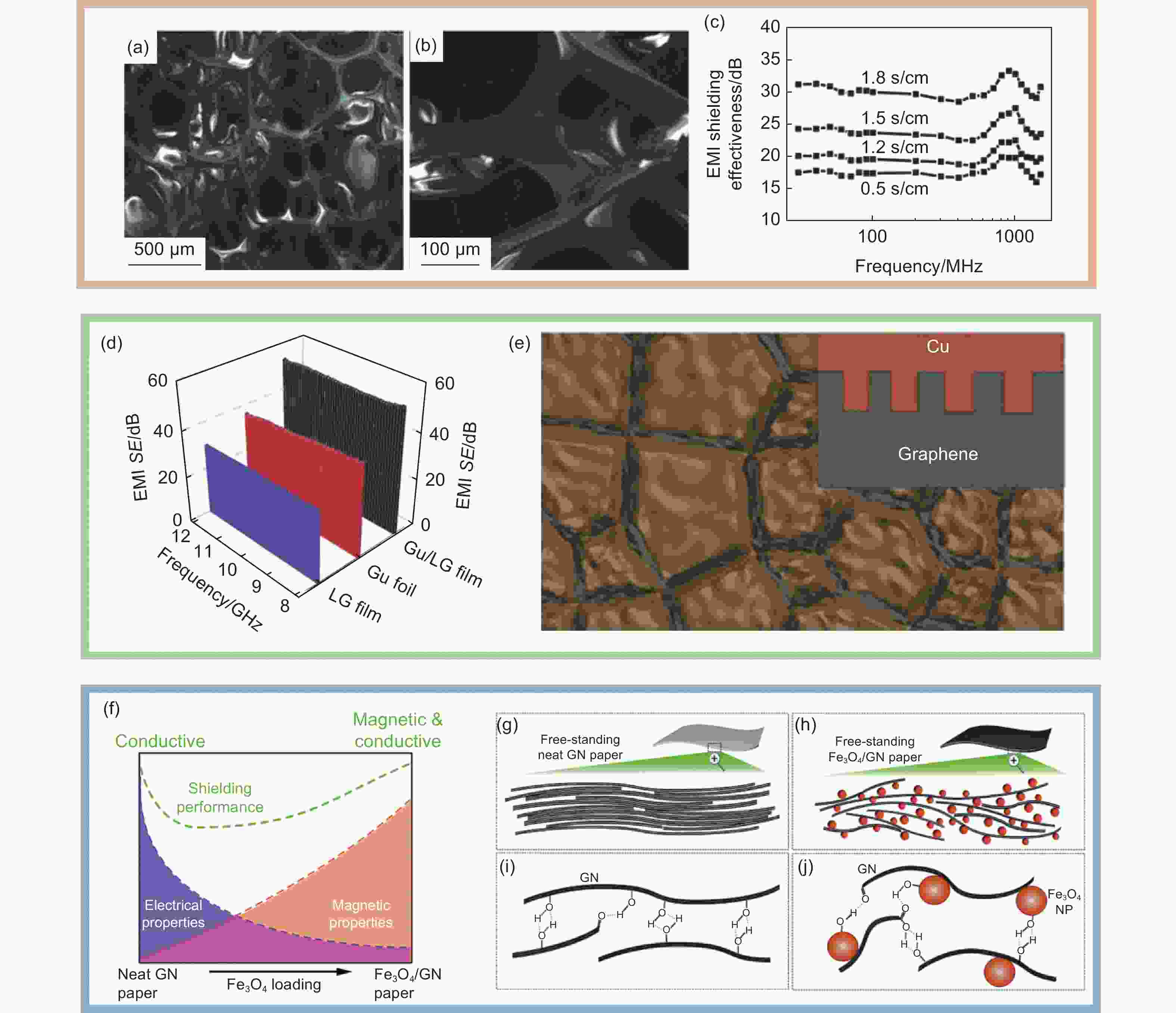
图 7 石墨烯基复合材料及其电磁屏蔽效能:(a,b)是具有3D互连网络结构的石墨烯/PDMS泡沫复合物的SEM照片;(c)30 MHz~1.5 GHz频率范围内测量的具有不同电导率的石墨烯/PDMS泡沫复合材料的电磁屏蔽效果[70]。(d)Cu箔、石墨烯膜和铜/石墨烯(Cu/LG)膜在Ku波段(12~18 GHz)的电磁屏蔽效能;(e)Cu/LG薄膜表面示意图和示意图[74]。(f)Fe3O4/GN片的屏蔽性能和电学和磁学性质变化的关系;(g)石墨烯纸的横截面示意图;(h)Fe3O4/GN纸的横截面示意图;(i)GN纸中GN层之间相互作用的可能机制;(j)Fe3O4/GN片之间的相互作用的可能机制[77]
Figure 7. Schematic diagram of the strategy and electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of composite heterogeneous materials: (a, b) SEM images of a foam composite, showing its 3D interconnected network structure. (c) EMI shielding effectiveness of graphene/PDMS foam composites with different electrical conductivities measured in frequency ranges of 30 MHz-1.5 GHz[70]. (d) The EMI SE of Cu foil, LG film, and Cu/LG film at Ku-band (12-18 GHz). (e) Diagrammatic sketch and schematic diagram (the inset) of Cu/LG film surface[73]. (f) Scheme of the shielding performance in the thin-layer GN-based papers: relationship with the changes in both electrical and magnetic properties. (g) Schemes of the cross-sectional illustrations of the free-standing GN paper. (h) Schemes of the cross-sectional illustrations of Fe3O4/GN paper. (i) Possible mechanism of the interactions between GN layers in the neat GN paper. (j) Possible mechanism of the interactions between Fe3O4/GN sheets[77]. Reprinted with permission
表 1 屏蔽效能值及其屏蔽效果[23]
Table 1. Shielding effectiveness and their shielding effects
SE值/dB 效果及应用 <30 差 ≥30,≤60 中等,可用于一般工业
或商业用电子设备>60,<90 良好,可用于航空航天及
军用仪器设备的屏蔽≥90 优,用于要求苛刻的
高精度﹑高敏感度产品表 2 石墨烯基电磁屏蔽材料调控策略及电磁屏蔽效能
Table 2. Summary of control strategies and EMW shielding effectiveness of graphene-based electromagnetic shielding materials
电磁屏蔽波段 策略 调控方式 样品 SE/dB 参考文献 9.3~9.8 GHz 二维结构化 吸收损耗 石墨烯定向组装薄膜 54.3 [36] 8.2~12.4 GHz 电导损耗 多孔石墨烯薄膜 40.0 [43] 8.2~12.4 GHz 三维结构化 多重反射/吸收损耗 石墨烯三维宏观体 64.1 [57] 8.2~12.4 GHz 吸收/多重反射损耗 石墨烯三维宏观体 68.8 [58] 8.2~12.4 GHz 异质原子掺杂 电导/介电损耗 氮掺杂石墨烯 >50.0 [64] 12~18 GHz 吸收/极化损耗 氟掺杂石墨烯 22.0 [68] 30 MHz~1.5 GHz 复合化 吸收/极化损耗 石墨烯/PDMS 30.0 [70] 8.0~12.0 GHz 极化/磁损耗 石墨烯-CNT-Fe2O3 130~134 [76] 1~18 GHz 电导/反射损耗 铜/石墨烯 52.0 [74] 0.2~0.3 THz 吸收/极化损耗 石墨烯/环氧树脂 70.0 [49] -
[1] Nan T, Lin H, Gao Y, et al. Acoustically actuated ultra-compact NEMS magnetoelectric antennas[J]. Nature Communications,2017,8(1):296-303. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00343-8 [2] Cheng J, Zhang H, Ning M, et al. Emerging materials and designs for low- and multi-band electromagnetic wave absorbers: The search for dielectric and magnetic synergy?[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2022,32(23):2200123-2200135. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202200123 [3] El-Saleh A A, Alhammadi A, Shayea I, et al. Measuring and assessing performance of mobile broadband networks and future 5G trends[J]. Sustainability,2022,14(2):829-842. doi: 10.3390/su14020829 [4] Chettri L, Bera R. A comprehensive survey on internet of things (IoT) toward 5G wireless systems[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal,2020,7(1):16-32. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2948888 [5] Shahzad F, Alhabeb M, Hatter C B, et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes)[J]. Science,2016,353(6304):1137-1140. doi: 10.1126/science.aag2421 [6] Ai B, Molisch A F, Rupp M, et al. 5G key technologies for smart railways[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE,2020,108(6):856-893. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2020.2988595 [7] Abdul-Al M, Amar A S I, Elfergani I, et al. Wireless electromagnetic radiation assessment based on the specific absorption rate (SAR): A review case study[J]. Electronics,2022,11(4):511-521. doi: 10.3390/electronics11040511 [8] Liu L, Deng H, Tang X, et al. Specific electromagnetic radiation in the wireless signal range increases wakefulness in mice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2021,118(31):e2105838118-e2105838124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2105838118 [9] González M, Pozuelo J, Baselga J. Electromagnetic shielding materials in GHz range[J]. The Chemical Record,2018,18(7-8):1000-1009. doi: 10.1002/tcr.201700066 [10] Yun T, Kim H, Iqbal A, et al. Electromagnetic shielding of monolayer MXene assemblies[J]. Advanced Materials,2020,32(9):1906769-1906800. doi: 10.1002/adma.201906769 [11] Cheng J, Li C, Xiong Y, et al. Recent advances in design strategies and multifunctionality of flexible electromagnetic interference shielding materials[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2022,14(1):80-110. doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00823-7 [12] Wang L, Huang M, Qian X, et al. Confined magnetic-dielectric balance boosted electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Small,2021,17(30):2100970-2100978. doi: 10.1002/smll.202100970 [13] Kruželák J, Kvasničáková A, Hložeková K, et al. Progress in polymers and polymer composites used as efficient materials for EMW shielding[J]. Nanoscale Advances,2021,3(1):123-172. doi: 10.1039/D0NA00760A [14] Cao M-S, Wang X-X, Zhang M, et al. Electromagnetic response and energy conversion for functions and devices in low-dimensional materials[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2019,29(25):1807398-1807452. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201807398 [15] Wu Z, Cheng H-W, Jin C, et al. Dimensional design and core–shell engineering of nanomaterials for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Advanced Materials,2022,34(11):2107538-2107567. doi: 10.1002/adma.202107538 [16] Chen H, Ma W, Huang Z, et al. Graphene-based materials toward microwave and terahertz absorbing stealth technologies[J]. Advanced Optical Materials,2019,7(8):1801318-1801333. doi: 10.1002/adom.201801318 [17] Shahzad F, Lee S H, Hong S M, et al. Segregated reduced graphene oxide polymer composite as a high performance electromagnetic interference shield[J]. Research on Chemical Intermediates,2018,44(8):4707-4719. doi: 10.1007/s11164-018-3274-7 [18] Xia Y, Gao W, Gao C. A review on graphene-based electromagnetic functional materials: Electromagnetic wave shielding and absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2022,32(42):2204591-2204626. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202204591 [19] Liu W, Speranza G. Tuning the oxygen content of reduced graphene oxide and effects on its properties[J]. ACS Omega,2021,6(9):6195-6205. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05578 [20] Cao M S, Wang X X, Zhang M, et al. Variable-temperature electron transport and dipole polarization turning flexible multifunctional microsensor beyond electrical and optical energy[J]. Advanced Materials,2020,32(10):1907156-1907163. doi: 10.1002/adma.201907156 [21] Li X H, Li X, Liao K N, et al. Thermally annealed anisotropic graphene aerogels and their electrically conductive epoxy composites with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding efficiencies[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(48):33230-33239. [22] Tan D, Jiang C, Li Q, et al. Development and current situation of flexible and transparent EM shielding materials[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2021,32(21):25603-25630. doi: 10.1007/s10854-021-05409-4 [23] Cao M, Han C, Wang X, et al. Graphene nanohybrids: Excellent electromagnetic properties for the absorbing and shielding of electromagnetic waves[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2018,6(17):4586-4602. doi: 10.1039/C7TC05869A [24] Liu L, Chen X, Wang J, et al. Effects of Y and Zn additions on electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of Mg-Y-Zn alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2019,35(6):1074-1080. [25] Pandey R, Tekumalla S, Gupta M. Enhanced (X-band) microwave shielding properties of pure magnesium by addition of diamagnetic titanium micro-particulates[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,770:473-482. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.08.147 [26] Choi H K, Lee A, Park M, et al. Hierarchical porous film with layer-by-layer assembly of 2D copper nanosheets for ultimate electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. ACS Nano,2021,15(1):829-839. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c07352 [27] Xu R, Wang W, Yu D. Preparation of silver-plated hollow glass microspheres and its application in infrared stealth coating fabrics[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings,2019,131:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.02.009 [28] Jin C, Lu Y, Tong G, et al. Excellent microwave absorbing properties of ZnO/ZnFe2O4/Fe core-shell microrods prepared by a rapid microwave-assisted hydrothermal-chemical vapor decomposition method[J]. Applied Surface Science,2020,531:147353-147363. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147353 [29] Liang H, Xing H, Qin M, et al. Bamboo-like short carbon fibers@Fe3O4@phenolic resin and honeycomb-like short carbon fibers@Fe3O4@FeO composites as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing materials[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2020,135:105959-105971. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.105959 [30] Song Q, Chen B, Zhou Z, et al. Flexible, stretchable and magnetic Fe3O4@Ti3C2Tx/elastomer with supramolecular interfacial crosslinking for enhancing mechanical and electromagnetic interference shielding performance[J]. Science China Materials,2021,64(6):1437-1448. doi: 10.1007/s40843-020-1539-2 [31] Chen Q, Zhang K, Huang L, et al. Reduced graphene oxide/MXene composite foam with multilayer structure for electromagnetic interference shielding and heat insulation applications[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials,2022,24(9):2200098-2200109. doi: 10.1002/adem.202200098 [32] Hong S K, Kim K Y, Kim T Y, et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of monolayer graphene[J]. Nanotechnology,2012,23(45):455704-455709. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/45/455704 [33] Long MQ, Tang L, Wang D, et al. Theoretical predictions of size-dependent carrier mobility and polarity in graphene[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2009,131(49):17728-17729. doi: 10.1021/ja907528a [34] Novoselov K S, Geim A K, Morozov S V, et al. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films[J]. Science,2004,306(5696):666-669. doi: 10.1126/science.1102896 [35] Cao M S, Wang X X, Cao W Q, et al. Ultrathin graphene: Electrical properties and highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2015,3(26):6589-6599. doi: 10.1039/C5TC01354B [36] Xu L, Zhang W, Wang L, et al. Large-scale preparation of graphene oxide film and its application for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. RSC Advances,2021,11(53):33302-33308. doi: 10.1039/D1RA06070H [37] Yang F, Xie P, Liu X, et al. High-orientation, defect-rich and porous graphene films for excellent electromagnetic shielding and thermal management[J]. Carbon,2023,214:118380-118387. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2023.118380 [38] Zhou E, Xi J, Guo Y, et al. Synergistic effect of graphene and carbon nanotube for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding films[J]. Carbon,2018,133:316-322. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.03.023 [39] Wei Q, Pei S, Qian X, et al. Superhigh electromagnetic interference shielding of ultrathin aligned pristine graphene nanosheets film[J]. Advanced Materials,2020,32(14):1907411-1907419. doi: 10.1002/adma.201907411 [40] Zhang L, Alvarez N T, Zhang M, et al. Preparation and characterization of graphene paper for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Carbon,2015,82:353-359. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2014.10.080 [41] Yin X, Li H, Han L, et al. Lightweight and flexible 3D graphene microtubes membrane for high-efficiency electromagnetic-interference shielding[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,387:124025-124035. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124025 [42] Lin J, Peng Z, Liu Y, et al. Laser-induced porous graphene films from commercial polymers[J]. Nature Communications,2014,5(1):5714-5721. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6714 [43] Xu J, Li R, Ji S, et al. Multifunctional graphene microstructures inspired by honeycomb for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding and wearable applications[J]. ACS Nano,2021,15(5):8907-8918. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c01552 [44] Shen B, Zhai W, Zheng W. Ultrathin flexible graphene film: An excellent thermal conducting material with efficient EMW shielding[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2014,24(28):4542-4548. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201400079 [45] Wang G, Zhao Y, Yang F, et al. Multifunctional integrated transparent film for efficient electromagnetic protection[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2022,14(1):65-78. doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00810-y [46] Xie Y, Liu S, Huang K, et al. Ultra-broadband strong electromagnetic interference shielding with ferromagnetic graphene quartz fabric[J]. Advanced Materials,2022,34(30):2202982-2202990. doi: 10.1002/adma.202202982 [47] Wang C, Xu Q, Hu J, et al. Graphene/SiC-coated textiles with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding, Joule heating, high-temperature resistance, and pressure-sensing performances[J]. Journal of Advanced Ceramics,2023,12(4):778-791. doi: 10.26599/JAC.2023.9220719 [48] Huang Z, Chen H, Huang Y, et al. Ultra-broadband wide-angle terahertz absorption properties of 3D graphene foam[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2018,28(2):1704363-1704371. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201704363 [49] Barani Z, Kargar F, Godziszewski K, et al. Graphene epoxy-based composites as efficient electromagnetic absorbers in the extremely high-frequency band[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(25):28635-28644. [50] 陈愚, 侯辉, 王连杰, 等. 电磁屏蔽材料在发射箱上的应用[J]. 包装工程,2008,29(12):270-271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3563.2008.12.102Chen Y, Hou H, Wang L J, et al. Application of electromagnetic shield material in launcher container[J]. Packaging Engineering,2008,29(12):270-271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3563.2008.12.102 [51] 杨薇弘, 张秋禹. 石墨烯基复合材料在空天领域的应用进展[J]. 固体火箭技术,2021,44(06):712-717. doi: 10.7673/j.issn.1006-2793.2021.06.002Yang W H, Zhang Q Y. Progress in graphene-based composites for aerospace applications[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology,2021,44(06):712-717. doi: 10.7673/j.issn.1006-2793.2021.06.002 [52] 张文博, 王佳宁, 卫林峰, 等. 功能型聚合物基电磁屏蔽材料的制备及应用[J]. 化学进展,2023,35(07):1065-1076. doi: 10.7536/PC221121Zhang W B, Wang J N, Wei L F, et al. Preparation and application of functional polymer-based electromagnetic shielding materials[J]. Progress in Chemistry,2023,35(07):1065-1076. doi: 10.7536/PC221121 [53] Gupta K, Nine M J, Denton C, et al. Electromagnetic shielding using graphene material in wide bandwidth of 1.5GHz-10GHz; proceedings of the 2022 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), F 31 Oct. -3 Nov. 2022, 2022 [C]. [54] Lan C, Zou L, Qiu Y, et al. Tuning solid–air interface of porous graphene paper for enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2020,55(15):6598-6609. doi: 10.1007/s10853-020-04433-9 [55] Zhang Y, Huang Y, Chen H, et al. Composition and structure control of ultralight graphene foam for high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Carbon,2016,105:438-447. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.04.070 [56] Shen B, Li Y, Yi D, et al. Microcellular graphene foam for improved broadband electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Carbon,2016,102:154-160. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.02.040 [57] Zhu E, Pang K, Chen Y, et al. Ultra-stable graphene aerogels for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Science China Materials,2023,66(3):1106-1113. doi: 10.1007/s40843-022-2208-x [58] Guo H, Hua T, Qin J, et al. A new strategy of 3D printing lightweight lamellar graphene aerogels for electromagnetic interference shielding and piezoresistive sensor applications[J]. Advanced Materials Technologies,2022,7(9):2101699-2101710. doi: 10.1002/admt.202101699 [59] Zhang H, Luo N, Liu T, et al. Light-weight, low-loading and large-sheet reduced graphene oxide for high-efficiency microwave absorber[J]. Carbon,2022,196:1024-1034. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2022.05.062 [60] 蔡乐, 王华平, 于贵. 石墨烯带隙的调控及其研究进展[J]. 物理学进展,2016,36(01):21-33.Cai L, Wang H P, Yu G. Modifying bandgap of graphene and its recent developments[J]. Progress in Physics,2016,36(01):21-33. [61] Błoński P, Tuček J, Sofer Z, et al. Doping with graphitic nitrogen triggers ferromagnetism in graphene[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2017,139(8):3171-3180. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b12934 [62] Xu J, Zhang X, Yuan H, et al. N-doped reduced graphene oxide aerogels containing pod-like N-doped carbon nanotubes and FeNi nanoparticles for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Carbon,2020,159:357-365. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.12.020 [63] Liu P, Zhang Y, Yan J, et al. Synthesis of lightweight N-doped graphene foams with open reticular structure for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,368:285-298. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.193 [64] 林少锋. 高可拉伸高导电化学交联和氮掺杂石墨烯薄膜及其电磁屏蔽性能研究 [D]; 国防科技大学, 2021.Lin S F. Stretchable chemically crosslinked and nitrogen doped graphene films with high electrical and electromagnetic shielding properties [D]; Graduate School of National University of Defense Technology, 2021. [65] Liu Y, Xu Z, Zhan J, et al. Superb electrically conductive graphene fibers via doping strategy[J]. Advanced Materials,2016,28(36):7941-7947. doi: 10.1002/adma.201602444 [66] Peng H, Ming X, Pang K, et al. Highly electrically conductive graphene papers via catalytic graphitization[J]. Nano Research,2022,15(6):4902-4908. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4130-z [67] Umrao S, Gupta T K, Kumar S, et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of boron and nitrogen co-doped reduced graphene oxide for the protection of electromagnetic radiation in Ku-Band[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(35):19831-19842. [68] Shahzad F, Zaidi S A, Koo C M. Synthesis of multifunctional electrically tunable fluorine-doped reduced graphene oxide at low temperatures[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(28):24179-24189. [69] Gavgani J N, Adelnia H, Zaarei D, et al. Lightweight flexible polyurethane/reduced ultralarge graphene oxide composite foams for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. RSC Advances,2016,6(33):27517-27527. doi: 10.1039/C5RA25374H [70] Chen Z, Xu C, Ma C, et al. Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Advanced Materials,2013,25(9):1296-1300. doi: 10.1002/adma.201204196 [71] Marka S K, Sindam B, James Raju K C, et al. Flexible few-layered graphene/poly vinyl alcohol composite sheets: Synthesis, characterization and EMW shielding in X-band through the absorption mechanism[J]. RSC Advances,2015,5(46):36498-36506. doi: 10.1039/C5RA04038H [72] Yousefi N, Sun X, Lin X, et al. Highly aligned graphene/polymer nanocomposites with excellent dielectric properties for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Advanced Materials,2014,26(31):5480-5487. doi: 10.1002/adma.201305293 [73] 刘伟, 贾琨, 谷建宇, 等. Ag/石墨烯复合薄膜的制备及其导热和电磁屏蔽性能研究[J]. 材料导报,2022,36(09):31-35. doi: 10.11896/cldb.21020136Liu W, Jia K, Gu J Y, et al. The preparation of Ag/graphene composite film for thermal conductionand electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Materials Reports,2022,36(09):31-35. doi: 10.11896/cldb.21020136 [74] Wang Z, Mao B, Wang Q, et al. Ultrahigh conductive copper/large flake size graphene heterostructure thin-film with remarkable electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness[J]. Small,2018,14(20):1704332-1704339. doi: 10.1002/smll.201704332 [75] Shu R, Zhang J, Wu Y, et al. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/cobalt–zinc ferrite composite aerogels with superior compression recovery and electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Nanoscale,2021,13(8):4485-4495. doi: 10.1039/D0NR08777G [76] Lee S H, Kang D, Oh I K. Multilayered graphene-carbon nanotube-iron oxide three-dimensional heterostructure for flexible electromagnetic interference shielding film[J]. Carbon,2017,111:248-257. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.10.003 [77] Song W L, Guan X T, Fan L Z, et al. Magnetic and conductive graphene papers toward thin layers of effective electromagnetic shielding[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2015,3(5):2097-2107. doi: 10.1039/C4TA05939E [78] Wang Y, Yao L, Zheng Q, et al. Graphene-wrapped multiloculated nickel ferrite: A highly efficient electromagnetic attenuation material for microwave absorbing and green shielding[J]. Nano Research,2022,15(7):6751-6760. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4428-x [79] Sadek R, Sharawi M S, Dubois C, et al. Reduced graphene oxide/barium ferrite ceramic nanocomposite synergism for high EMW wave absorption[J]. ACS Omega,2023,8(17):15099-15113. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c08168 [80] Wan Y J, Zhu P L, Yu S H, et al. Graphene paper for exceptional EMW shielding performance using large-sized graphene oxide sheets and doping strategy[J]. Carbon,2017,122:74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.06.042 [81] Zhao Y, Hao L, Zhang X, et al. A novel strategy in electromagnetic wave absorbing and shielding materials design: Multi-responsive field effect[J]. Small Science,2022,2(2):2100077-2100092. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202100077 [82] Clancy A J, Au H, Rubio N, et al. Understanding and controlling the covalent functionalisation of graphene[J]. Dalton Transactions,2020,49(30):10308-10318. doi: 10.1039/D0DT01589J [83] Zhang M, Han C, Cao W Q, et al. A nano-micro engineering nanofiber for electromagnetic absorber, green shielding and sensor[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2020,13(1):27-39. [84] Huang L, Duan Y, Dai X, et al. Bioinspired metamaterials: Multibands electromagnetic wave adaptability and hydrophobic characteristics[J]. Small,2019,15(40):1902730-1902737. doi: 10.1002/smll.201902730 -





 下载:
下载: