Electrochemical method for impurity removal of graphite anode in spent ternary lithium-ion batteries
-
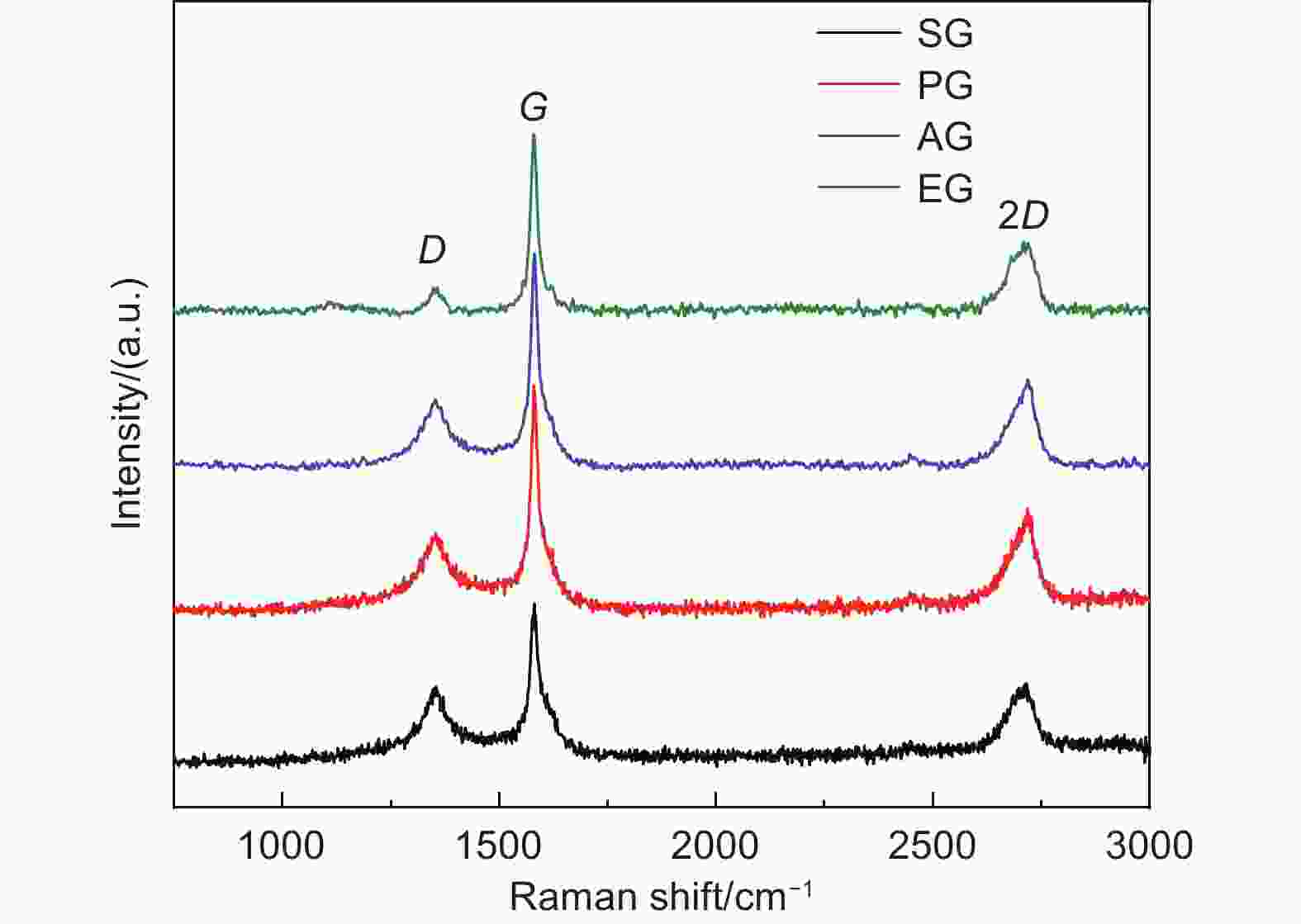
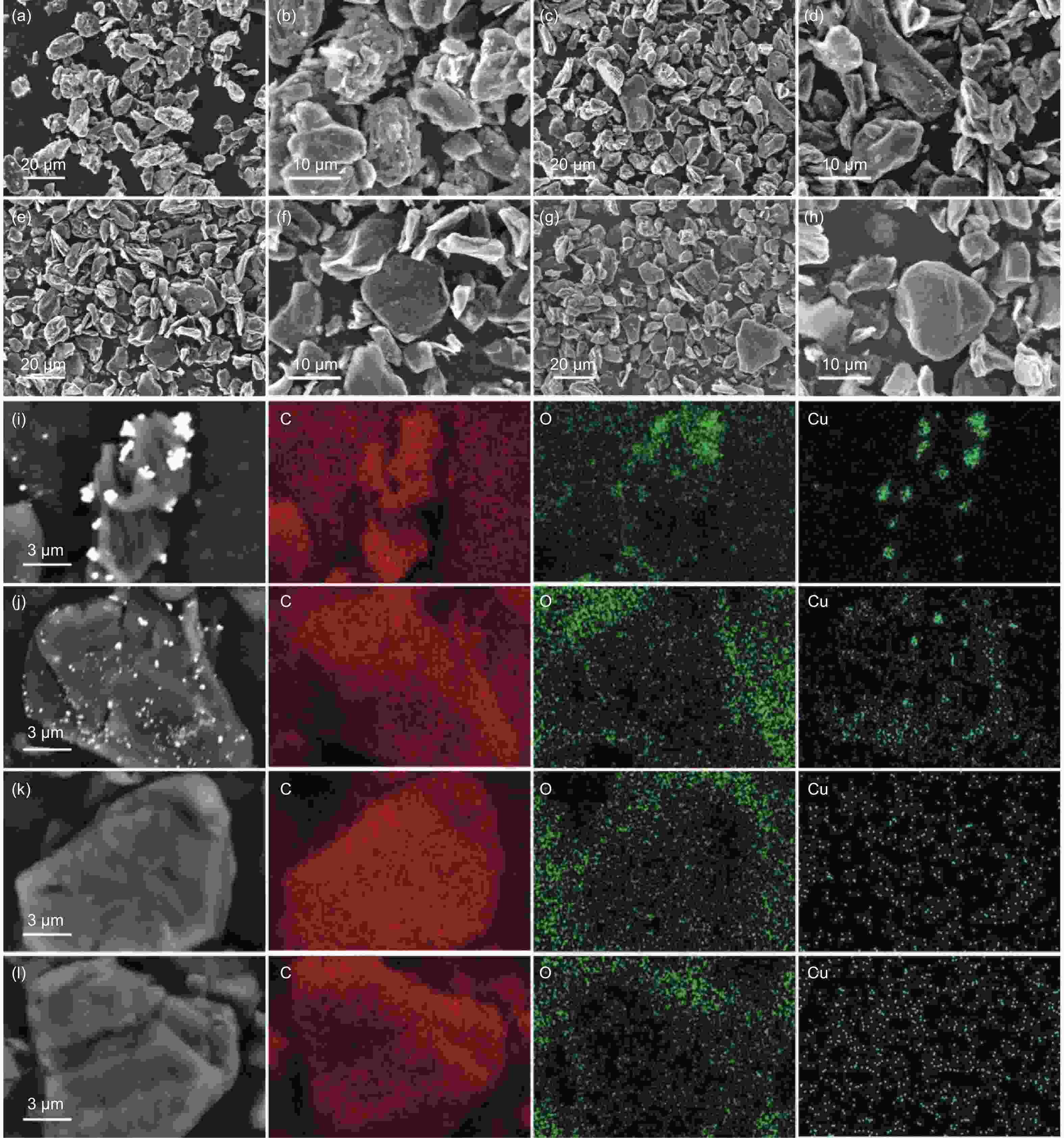
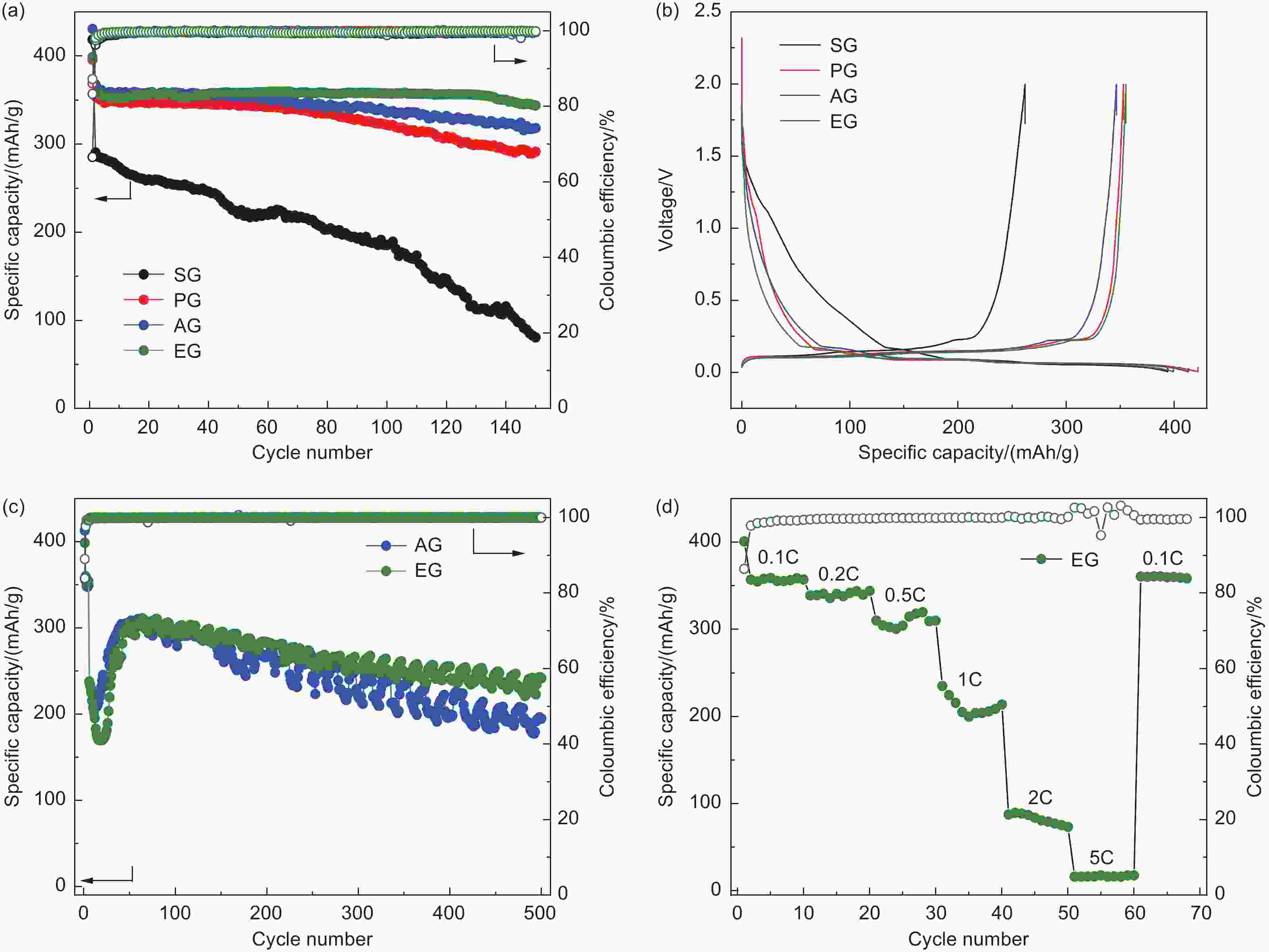
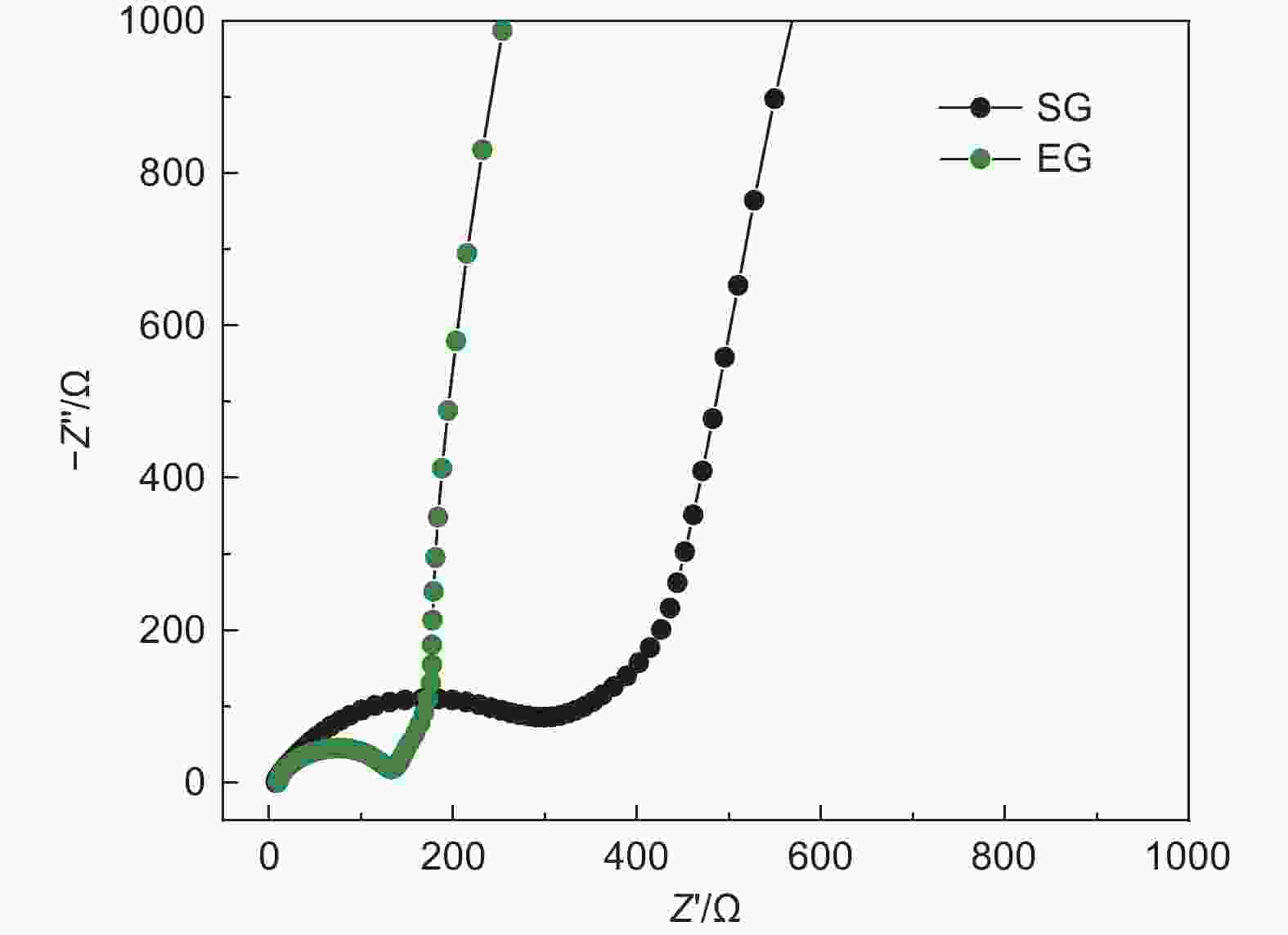
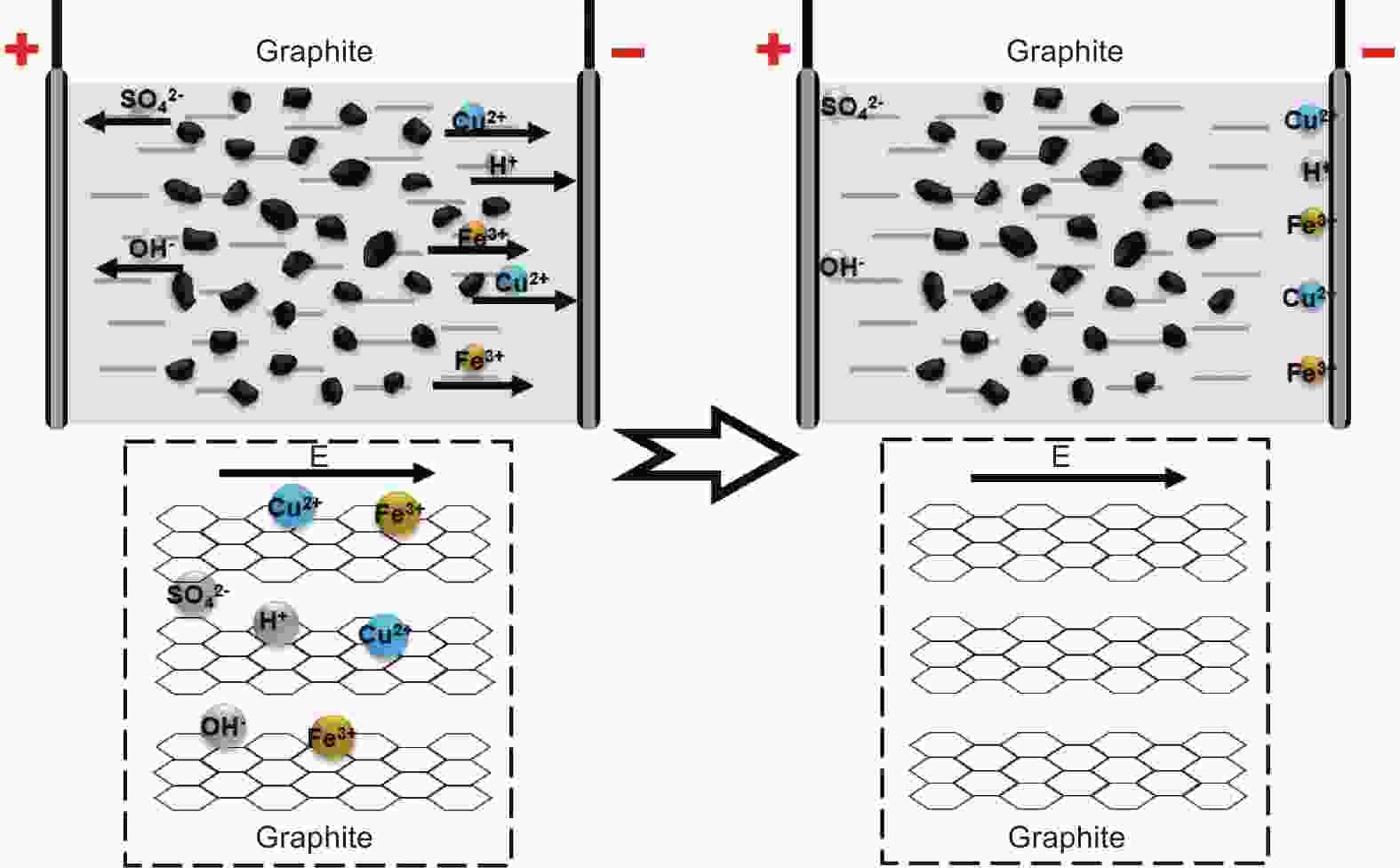
摘要: 随着新能源汽车迅速发展,动力锂离子电池应用越来越广泛,大量锂电池也迎来退役高峰期,废旧锂电池的回收综合利用引起各国高度关注。废旧锂电池石墨负极层状结构基本未变化,因此回收时不需高温石墨化,只需关注其内部杂质的去除。本文将废旧石墨负极热处理、超声分离和酸浸处理后,创新性地采用电化学处理将内部金属杂质深度去除。对比不同回收阶段的石墨,发现石墨中有机杂质的存在会严重影响各项电化学性能,微量Cu、Fe等无机杂质的存在对初始放电比容量影响不大,但会降低石墨的循环稳定性。最终回收的石墨内部主要金属杂质含量低于20 mg/kg,在0.1 C倍率下放电比容量达到358.7 mAh/g,循环150圈后容量保持率为95.85%。对比已报道的废旧石墨回收方法,此方法可深度去除石墨负极内部杂质,解决了目前酸碱用量大、除杂不彻底、能耗高等问题,回收再生石墨负极电化学性能较好,为废旧锂电池石墨负极提供了一条新的回收再生路径。Abstract: The application of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) is becoming increasingly widespread, and a large number of LIBs are entering the peak period of retirement. The recycling and comprehensive utilization of spent LIBs has attracted high attention from countries around the world. Due to the graphite anode in spent LIBs, it’s recycling does not require high-temperature graphitization, the unchanged layered structure of and only focuses on the removal of internal impurities. In this study, we innovatively used electrochemical treatment to deeply remove internal metal impurities after heat treatment, ultrasonic separation and acid leaching of spent graphite. By comparing and analyzing the graphite in different recovery stages, it is found that the presence of organic impurities in graphite will seriously affect the electrochemical performance. The presence of trace inorganic impurities such as Cu and Fe has little effect on the initial discharge specific capacity, but it will reduce the cycle stability of graphite. The content of main metal impurities in the final recycled graphite is less than 20 mg/kg. The discharge specific capacity reaches 358.7 mAh/g at 0.1 C, and the capacity remains 95.85% after 150 cycles. Compared with the reported methods for recycling spent graphite, this method can deeply remove impurities inside the graphite, solve the current problems of high acid and alkali consumption, incomplete impurity removal and high energy consumption. The recycled graphite anode shows good electrochemical performance, which provides, a new recycling and regeneration path for spent LIBs graphite anode.
-
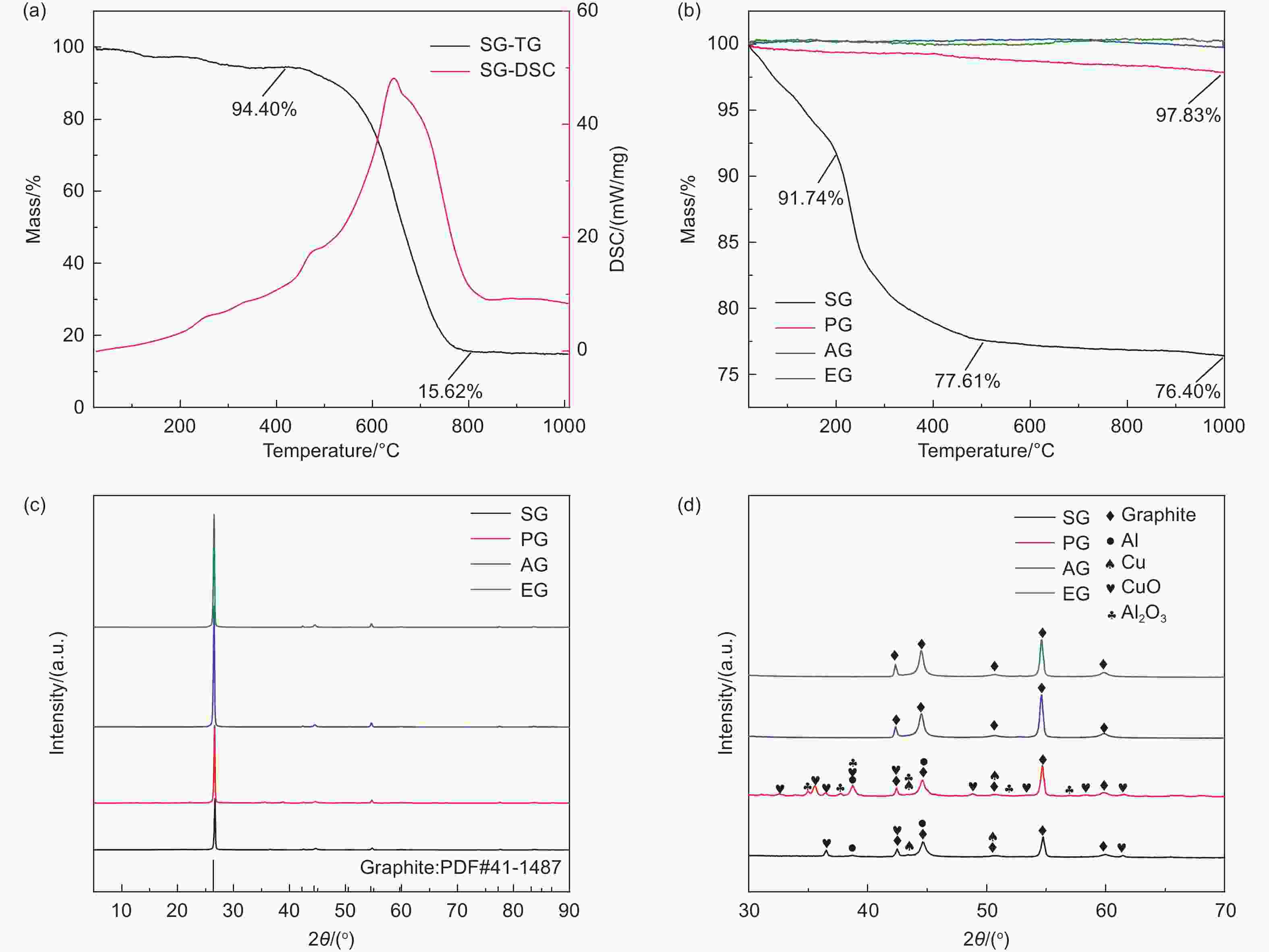
表 1 SG、AG和EG的ICP检测结果/(mg/kg)
Table 1. Characterization of SG, AG and EG by ICP /(mg/kg)
Li Al Cu Ni Co Mn Fe SG 13309 521 4860 639 231 340 219 AG 519 68 1012 8 <5 <5 116 EG 81 13 14 <5 <5 <5 13 -
[1] Wu N N, Wu K, Gao Y, et al. Advantages of lithium ion batteries in energy storage field[J]. Advance Materials Industry,2010(10):48. [2] Yang J, Jiang L X, Liu F Y, et al. Reductive acid leaching of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries using hydrazine sulfate as reductant[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2020,30:2256-2264. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65376-6 [3] Contestabile M, Panero S, Scrosati B. A laboratory-scale lithium-ion battery recycling process[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2001,92(1-2):65-69. doi: 10.1016/S0378-7753(00)00523-1 [4] Wohlfahrt-Mehrens M, Vogler C, Garche J. Aging mechanisms of lithium cathode materials[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2004,127(1-2):58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2003.09.034 [5] Wang H, Jang Y I, Huang B, et al. TEM study of electrochemical cycling-induced damage and disorder in LiCoO2 cathodes for rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society,1999,146(2):473-480. doi: 10.1149/1.1391631 [6] Arora P, White R E, Doyle M. Capacity fade mechanisms and side reactions in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society,1998,145(10):3647-3667. doi: 10.1149/1.1838857 [7] Sloop S E, Pugh J K, Wang S, et al. Chemical reactivity of PF5 and LiPF6 in ethylene carbonate/dimethyl carbonate solutions[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters,2004,4(4):A42-A44. [8] Murphy S J, Grigahcene A, Niemczura E, et al. Corrosion of lithium-ion battery current collectors[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society,1999,146(2):448-456. doi: 10.1149/1.1391627 [9] Bai Y C, Muralidharan N, Sun Y K, et al. Energy and environmental aspects in recycling lithium-ion batteries: Concept of battery identity global passport[J]. Materials Today,2020,41:304-15. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2020.09.001 [10] 杨涛, 刘文凤, 马梦月, 等. 三元锂离子动力电池衰减机理[J]. 应用化学,2020,37(10):1181-1186. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2020.10.200116Yang T, Liu W F, Ma M Y, et al. Fade mechanism of ternary lithium ion power battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry,2020,37(10):1181-1186. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2020.10.200116 [11] 阮一钊, 田艳红, 李守涛, 等. LiNi0. 5Co0.2Mn0.3O2/石墨电池高温失效的机理[J]. 电池,2020,50(03):220-223.Ruan Y Z, Tian Y H, Li S T, et al. High temperature failure mechanism of LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2/graphite battery[J]. Battery Bimonthly,2020,50(03):220-223. [12] Bi H J, Zhu H B, Zu L, et al. Combined mechanical process recycling technology for recovering copper and aluminium components of spent lithium-iron phosphate batteries[J]. Waste Management & Research:the Journal of the International Solid Wastes and Public Cleansing Association, ISWA,2019,37(8):767-780. [13] Wang F F, Zhang T, He Y Q, et al. Recovery of valuable materials from spent lithium-ion batteries by mechanical separation and thermal treatment[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2018,185:646-652. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.069 [14] Zhang G W, He Y Q, Feng Y, et al. Enhancement in liberation of electrode materials derived from spent lithium-ion battery by pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2018,199:62-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.143 [15] Liu K, Yang S L, Luo L Q, et al. From spent graphite to recycle graphite anode for high-performance lithium ion batteries and sodium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2020,356:136856. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136856 [16] Natarajan S, Shanthana L D, Bajaj H C, et al. Recovery and utilization of graphite and polymer materials from spent lithium-ion batteries for synthesizing polymer-graphite nanocomposite thin films[J]. Journal of Enviromental Chemical Engineering,2015,3(4):2538-2545. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2015.09.011 [17] Yang Y, Song S L, Lei S Y, et al. A process for combination of recycling lithium and regenerating graphite from spent lithium-ion battery[J]. Waste Management,2019,85:529-537. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.01.008 [18] Zhang J, Li X L, Song D W, et al. Effective regeneration of anode material recycled from scrapped Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2018,390:38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.04.039 [19] Yang K, Gong P Y, Tian Z L, et al. Recycling spent carbon cathode by a roasting method and its application in Li-ion batteries anodes[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,261:121090-121090. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121090 [20] Zhang J, Li X L, Song D W, et al. Effective regeneration of anode material recycled from scrapped Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2018,390:38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.04.039 [21] Wang A P, Kadam S, Li H, et al. Review on modeling of the anode solid electrolyte interphase(SEI) for lithium-ion batteries[J]. npj Computational Materials,2018,4(1):359-367. [22] Ma Z, Zhuang Y C, Deng Y M, et al. From spent graphite to amorphous sp2+sp3 carbon-coated sp2 graphite for high-performance lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2018,376:91-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.11.038 [23] Wang H R, Huang Y S, Huang C F, et al. Reclaiming graphite from spent lithium ion batteries ecologically and economically[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2019,313:423-431. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2019.05.050 [24] Huang Q, Ni S, Jiao M, et al. Aligned carbon-based electrodes for fast-charging batteries: A Review[J]. Small,2021,17(48):2007676-2007701. doi: 10.1002/smll.202007676 [25] Wang G, Pan C, Wang L P, et al. Activated carbon nanofiber webs made by electrospinning for capacitive deionization[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2012,69:65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.02.066 [26] Shao H, Wu Y C, Lin Z F, et al. Nanoporous carbon for electrochemical capacitive energy storage[J]. Chemical Society Reviews,2020,49(10):3005-3039. doi: 10.1039/D0CS00059K -





 下载:
下载: